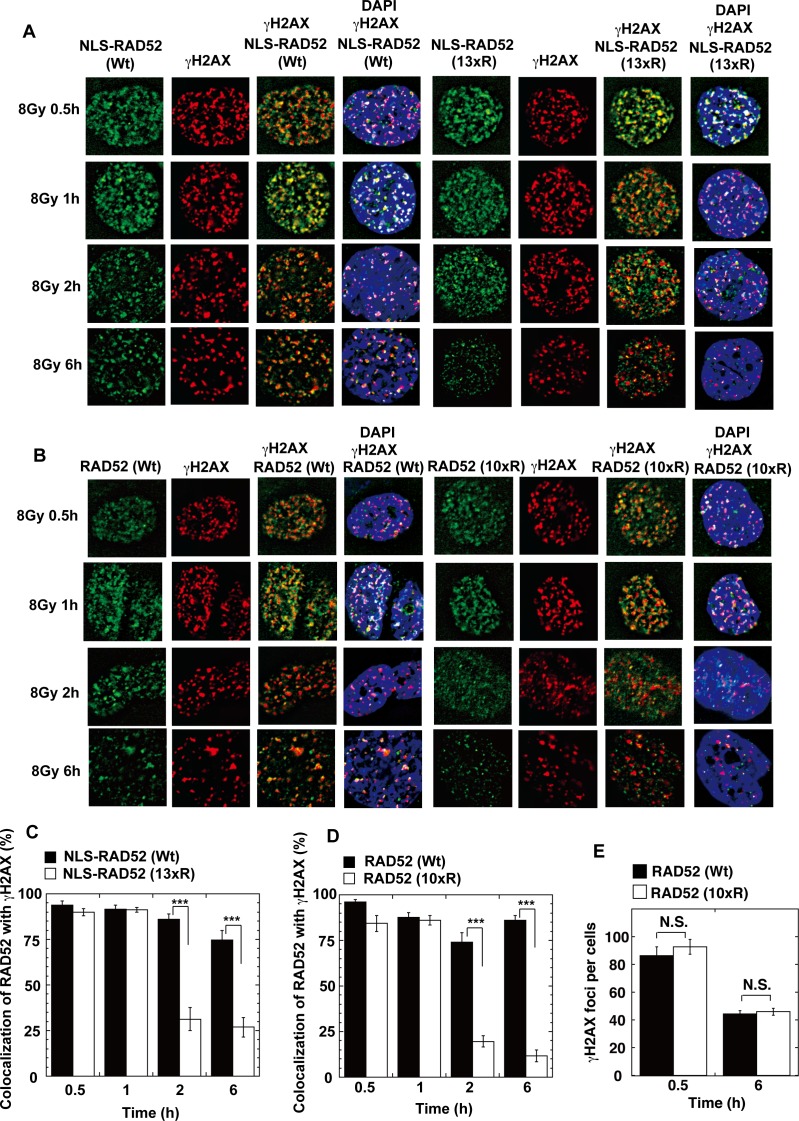
Fig 9. Effect of acetylation-deficient mutations on ionizing radiation-induced foci formation by RAD52.
(A, B) MSCs stably expressing FLAG-RAD52-HA proteins were irradiated with γ-rays (8 Gy). At the indicated time after irradiation, the cells were subjected to immunofluorescent staining with an anti-HA (green) antibody, an anti-γH2AX (red) antibody, and DAPI (blue). (A) MSCs expressing NLS-RAD52 (Wt) or NLS-RAD52 (13xR) were used. (B) MSCs expressing RAD52 (Wt) or RAD52 (10xR) were used. (C, D) The percentages of RAD52 foci colocalized with γH2AX were calculated, as described in the Supporting Materials and Methods. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between the indicated pairs of groups (***, p<0.001 by t-test). (E) The number of γH2AX foci per cell was counted in MSCs expressing RAD52 (Wt) or RAD52 (10xR) at the indicated time after irradiation with γ-rays (8 Gy), as described in the Supporting Materials and Methods (N.S., not significant by t-test).