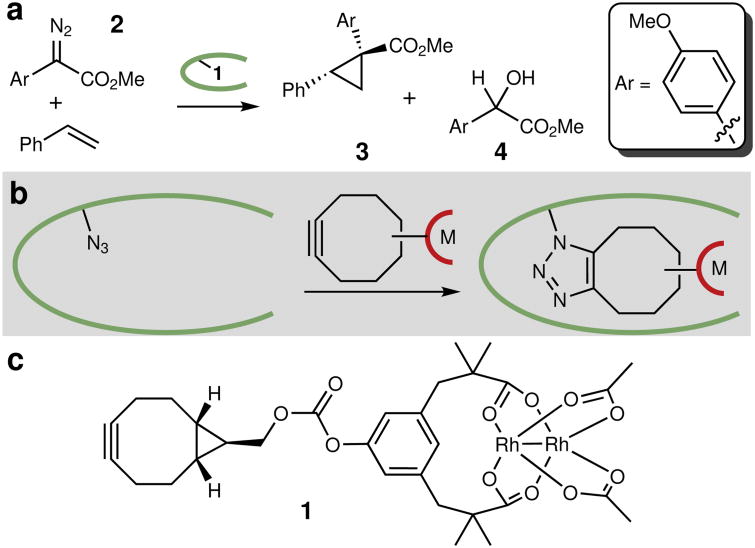
Figure 1. Model reaction and ArM structure.
a , Model cyclopropanation reaction used for ArM evolution. The dirhodium cofactor catalyzes diazo decomposition to generate a rhodium carbenoid intermediate that can insert into the olefin π bond or (because the reactions are carried out in aqueous solution) the water O-H bond. The protein scaffold provides chemoselectivity and enantioselectivity. Reactions conducted using 22 mM styrene, 4.4 mM diazo, and 1 mol% ArM in 10% v/v THF/50 mM PIPES (pH 7.4) containing 1.75 M NaBr at 4 °C. b, ArM formation via SPAAC19 between bicyclononyne-substituted metal complexes and a genetically encoded 4-l-azidophenylalnine residue, allowing covalent attachment of the cofactor, even in cellular lysate. c, Structure of dirhodium cofactor 1.