Figure 2.
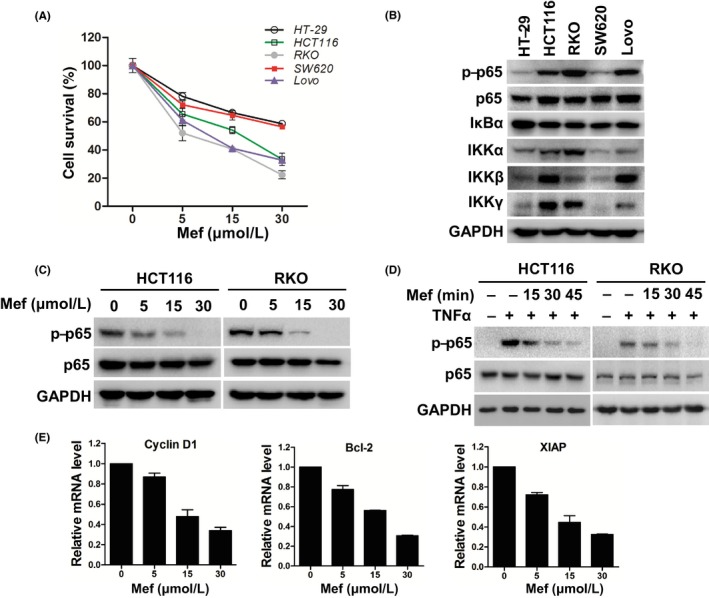
Mefloquine (Mef) suppresses nuclear factor kappa B (NF‐κB) activity in colorectal cancer cells. A, CRC cells HT‐29, HCT116, RKO, SW620 and Lovo were treated with the indicated concentrations of mefloquine for 24 h. Their viability was then measured by CCK‐8 assay. B, Immunoblotting analysis of NF‐κB signaling components p‐p65, p65, IKBα, IKKα, IKKβ, and IKKγ in the 5 lines of CRC cells. GAPDH was used as a loading control. C, After exposure to increased concentrations of mefloquine overnight, HCT116 and RKO cells were lysed and analyzed by immunoblotting against p‐p65 and p65. GAPDH was used as a loading control. D, Following starvation overnight in serum‐free medium, HCT116 and RKO cells were incubated with 30 μmol/L mefloquine for the indicated times, then stimulated with tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF‐α; 50 ng/mL) for 20 min. The cells were lysed and analyzed by immunoblotting of p‐p65, p65 and GAPDH. E, mRNA levels of Cyclin D1, Bcl‐2 and XIAP were measured by qRT‐PCR in RKO cells treated with 0, 5, 15 or 30 μmol/L mefloquine overnight. IKK, IκB kinase
