Figure 3.
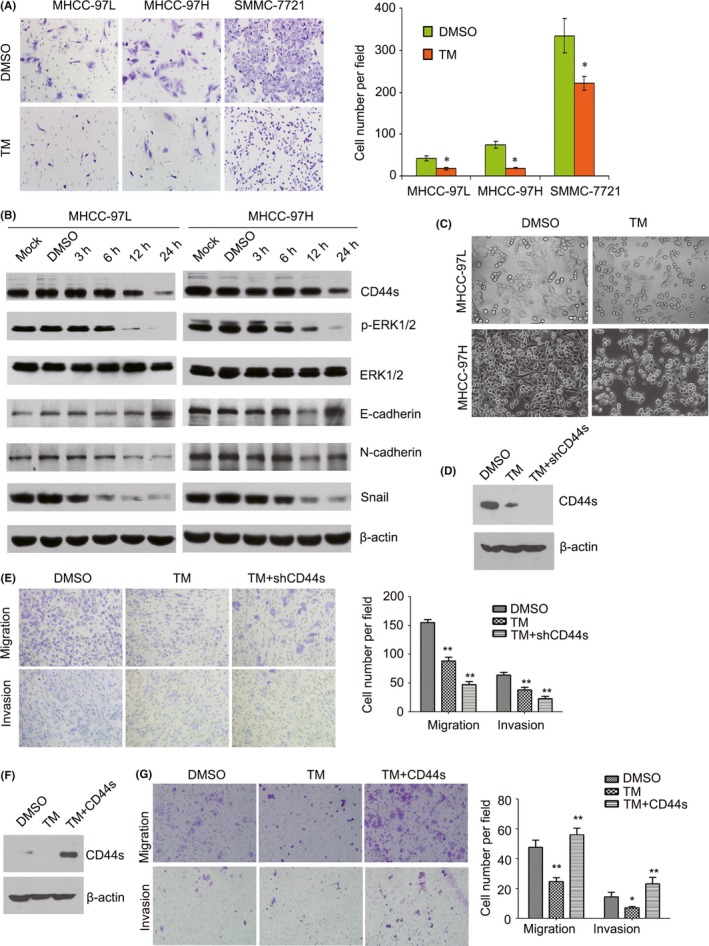
Tunicamycin (TM) inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell migration through the CD44s and ERK1/2 pathway. A, Following treatment of MHCC‐97L, MHCC‐97H and SMMC‐7721 cells with 2.5 μg/mL TM for 48 h, cell migration was detected by transwell assay. *P < .05. B, Expression of CD44s, p‐ERK1/2, ERK1/2, E‐cadherin, N‐cadherin and Snail was detected by western blotting in MHCC‐97L and MHCC‐97H cells treated with 2.5 μg/mL TM for the indicated length of time. C, Phase‐contrast images (200×) show morphological changes in TM‐treated MHCC‐97L and MHCC‐97H cells and control cells. D, Expression of CD44s was detected by western blotting in CD44s knockdown MHCC‐97L cells or control cells treated with 2.5 μg/mL TM for 12 h. E, Migration and invasion were measured using transwell assays with CD44s knockdown MHCC‐97L cells or control cells treated with 2.5 μg/mL TM. **P < .01. F, Expression of CD44s was detected by western blotting in CD44s overexpressing PLC/PRF/5 cells or control cells treated with 2.5 μg/mL TM for 12 h. G, Migration and invasion were measured using transwell assays with CD44s overexpressing PLC/PRF/5 cells or control cells treated with 2.5 μg/mL TM. *P < .05; **P < .01
