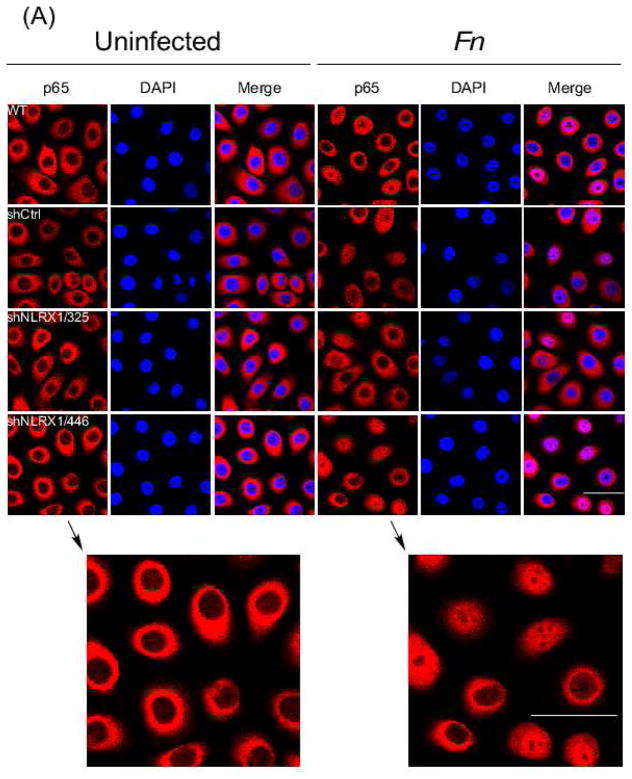
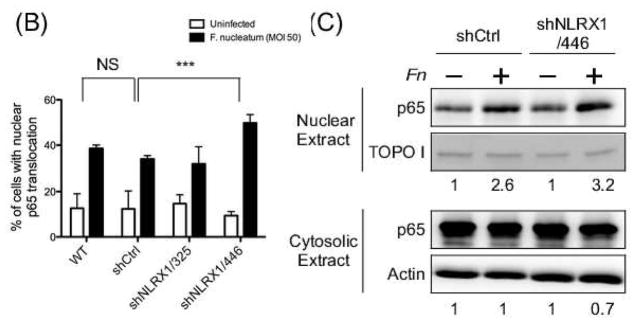
Fig. 6. NLRX1 regulated F. nucleatum-elicited NF-κB nuclear translocation.
(A) Confocal microscopy of GECs uninfected or infected with F. nucleatum at an M.O.I. of 50 for 1h followed by fixation. Cells were then immunostained with anti-NF-κB p65 (red) and stained nuclei with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of fluorescence microscopy images obtained under condition as in (A). Fluorescence intensity of p65 in nuclei and total cells was measured by CellProfiler. Statistical significance was determined using two-way ANOVA. ***P< 0.001. (C) Nuclear and cytosol fraction of cells were isolated followed by immunoblotting using anti-NF-κB p65 antibody. TOPO I and actin served as loading control for nuclear and cytosol fractions, separately. All data are representative of at least three independent experiments performed in duplicates.