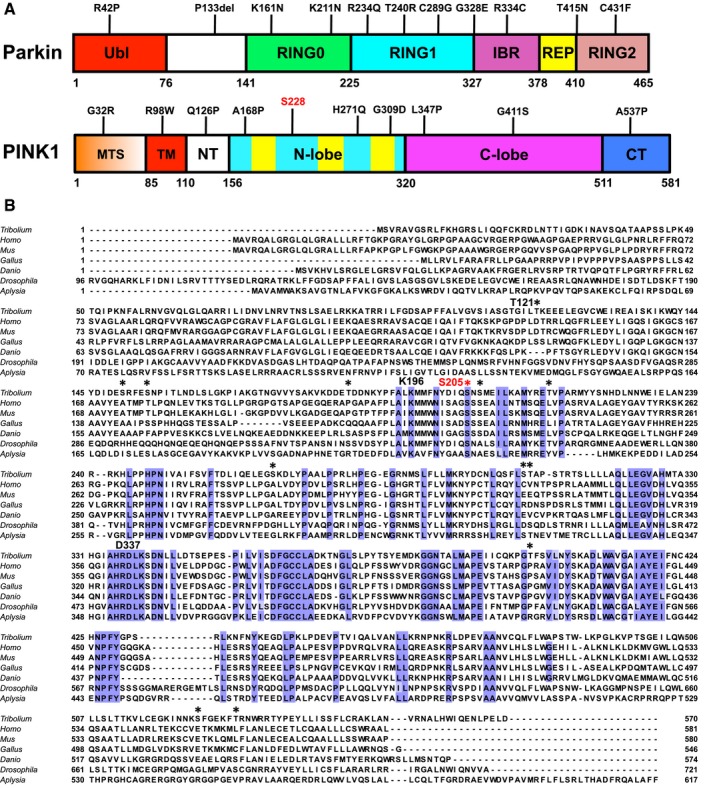
Multiple sequence alignment of PINK1 orthologs;
Tribolium castaneum (Tc, red beetle),
Homo sapiens (human),
Mus musculus (mouse),
Gallus gallus (chicken),
Danio rerio (zebra fish),
Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly), and
Aplysia californica (sea slug). The alignment shows residues conserved across all species (blue), sites of autophosphorylation found in purified TcPINK1 are indicated with *. Ser205 is colored in red, and active site residues Lys196 and Asp337 are indicated. The alignment was performed using the MUSCLE server (
https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/muscle/) for the segment corresponding to TcPINK1
121–570. The N‐terminal segments (corresponding to TcPINK1
1–120) have low conservation and were not aligned for better visual display of their lengths.