Figure EV1. Genomic localisation of ZBTB2 in mouse embryonic stem cells in vivo (related to Fig 1).
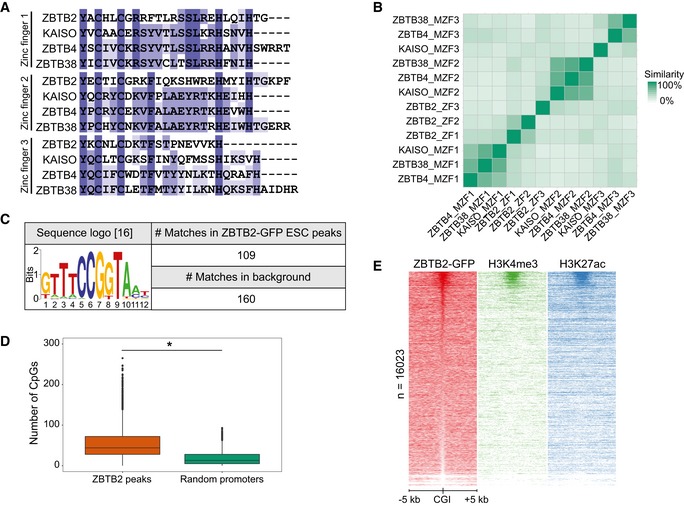
- Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the zinc finger domains of ZBTB2 and the evolutionarily conserved methyl‐CpG‐binding zinc fingers of KAISO and KAISO‐like proteins.
- Matrix of the percentage similarity between each of the zinc finger domains depicted in (A). (M)ZF = (methyl)zinc finger.
- Sequence logo of a recently reported ZBTB2‐binding motif 16 and its occurrence in the called ZBTB2 ChIP‐seq peaks in ESCs and a background consisting of all mouse CGIs.
- The number of CpG dinucleotides counted in the sequences of the ZBTB2 ChIP‐seq peaks in ESCs and in a set of random promoters (n = 4,072) of the same average length (*P < 2.2e‐16, Welch t‐test). Box: median (central line), first and third quartile (box limits); whiskers: 1.5 × interquartile range.
