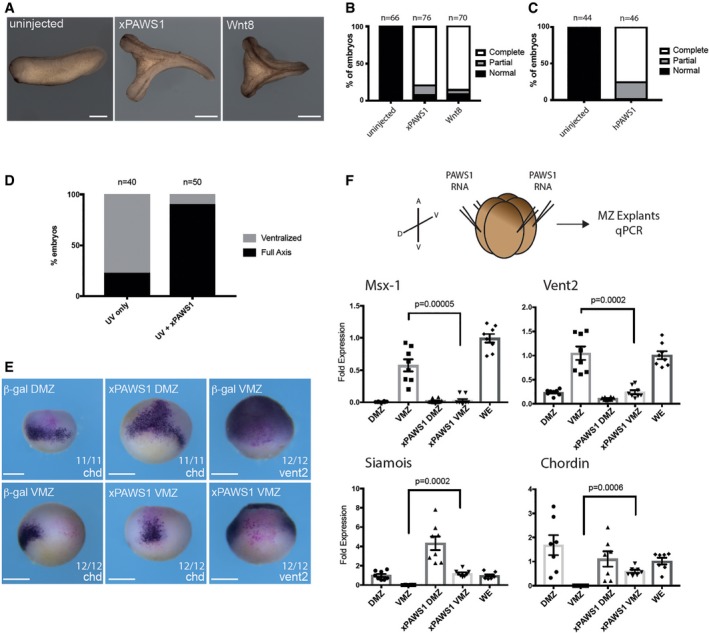
Representative images of an uninjected embryo, and embryos injected with 250 pg xPAWS1 mRNA or 5 pg xWnt8 mRNA. Scale bars are 1 mm.
Quantification of (A). Complete axis denotes embryos with a secondary axis with a cement gland, while a partial axis does not.
Quantification of axis‐inducing activity of 250 pg of hPAWS1.
250 pg of xPAWS1 mRNA rescues UV‐ventralised embryos.
xPAWS1 induces dorsal and represses ventral gene expression in the whole embryo. A single blastomere at the four‐cell stage was injected with either 200 pg nuclear β‐gal mRNA alone or with 250 pg of xPAWS1 and 200 pg of nuclear β‐gal mRNA. At stage 10, embryos were fixed, stained for β‐gal and then developed for in situ hybridisation using probes specific for Chordin or Vent2. In dorsal blastomeres, xPAWS1 induces expression of Chordin, while in ventral blastomeres it represses Vent2 expression. The number of embryos tested is indicated. Scale bars are 500 μm.
250 pg of xPAWS1 and 200 pg of CFP_gpi mRNAs was injected into the marginal zone of each blastomere at the four‐cell stage. The dorsal/ventral (D/V) and animal/vegetal (A/V) axes are indicated. At stage 10, the dorsal marginal zone (DMZ) and ventral marginal zone (VMZ) were isolated and dorsal and ventral marker expression was assessed by qPCR. xPAWS1 inhibits ventral marker expression (Msx‐1 and Vent2), while concomitantly upregulating the dorsal markers Chordin and Siamois in the VMZ. Expressions of Msx‐1, Vent2, Siamois, and Chordin were normalised to the expression levels of Histone H4, and presented as a fold change with respect to the average levels in whole embryos (WE), (n = 8, error bars represent ± SEM; t‐test, unpaired, two‐tailed with unequal variance Mann–Whitney test, P‐values are as indicated).