Figure EV2. PAWS1 is phosphorylated at Ser614 by CK1α in vitro .
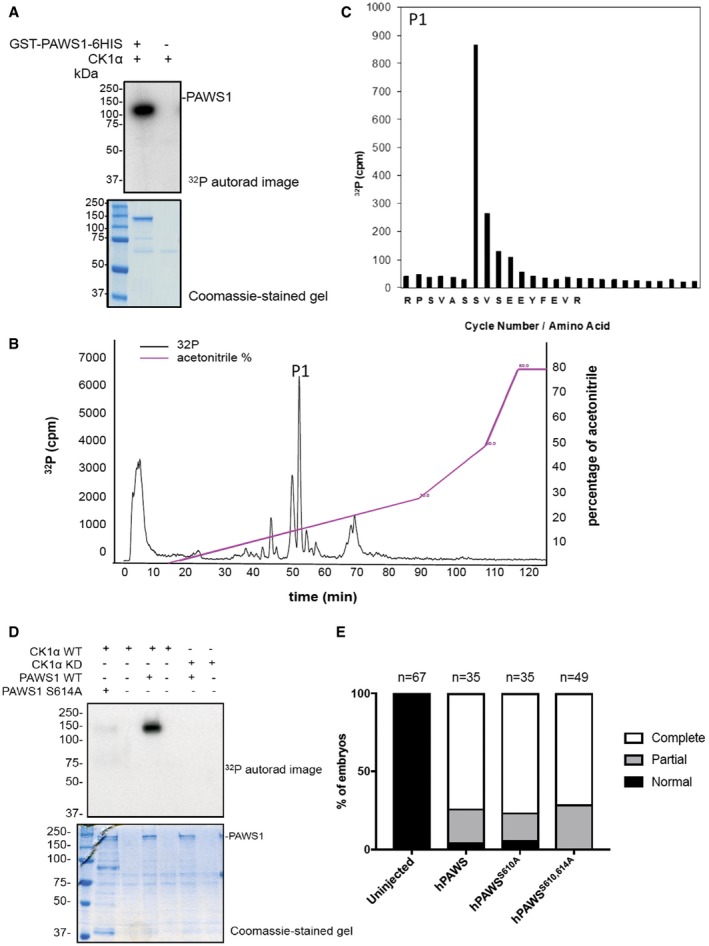
- 32P autoradiography and Coomassie stain of SDS–PAGE gel after an in vitro kinase assay with GST‐CK1α and GST‐PAWS1‐6xHis as a substrate.
- GST‐PAWS1‐6xHis phosphorylated by CK1α in A was excised from the gel, digested with trypsin and resolved by HPLC on a C18 column using increasing acetonitrile gradient. Analysis of the [γ32P] radioactivity peak at 54.1 min (P1) by LC‐MS/MS revealed the phospho‐peptide RPSVASSVSEEYFEVR.
- Analysis of the [γ32P] radioactivity peak P1 by LC‐MS/MS revealed various phospho‐peptides, of which RPSVASS(P)VSEEYFEVR was the only one to match the solid‐phase Edman sequencing data. Together, they reveal that CK1α phosphorylates PAWS1 at Ser614.
- 32P autoradiography and Coomassie stain of SDS–PAGE after an in vitro kinase assay with CK1αWT or CK1αKD (kinase dead) and PAWS1WT or PAWS1S614A as substrates.
- Human PAWS1WT, hPAWS1S610A and hPAWS1S610A/S614A induce axis duplication in Xenopus embryos.
