FIGURE 3.
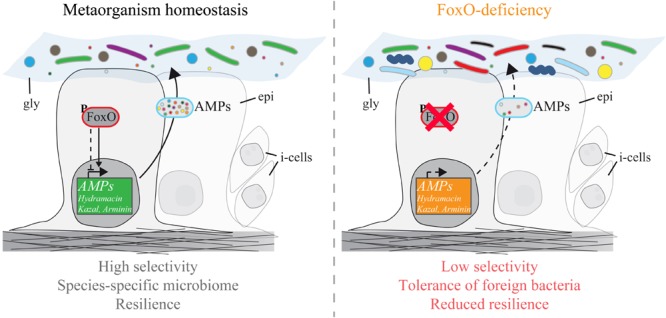
Schematic representation showing the effect of FoxO on AMP expression and metaorganism homeostasis. (Left) In a state of intact FoxO signaling and metaorganism homeostasis, FoxO acts as an activator on the expression of AMPs of the families Hydramacin, Kazal, and Arminin in the epithelial tissue (epi). This results in a unique cocktail of AMPs in the glycocalyx (gly) of the animals, shaping the microbiome in a species-specific manner. (Right) FoxO deficiency reduces the overall expression of AMPs. Decreased levels of AMPs reduce the host selection over symbiotic bacteria colonizing the glycocalyx. Due to a higher tolerance an increased diversity of non-species-specific bacteria can settle. This demonstrates impairment in microbiome resilience and metaorganism homeostasis caused by FoxO deficiency. i-cells: interstitial stem cells.
