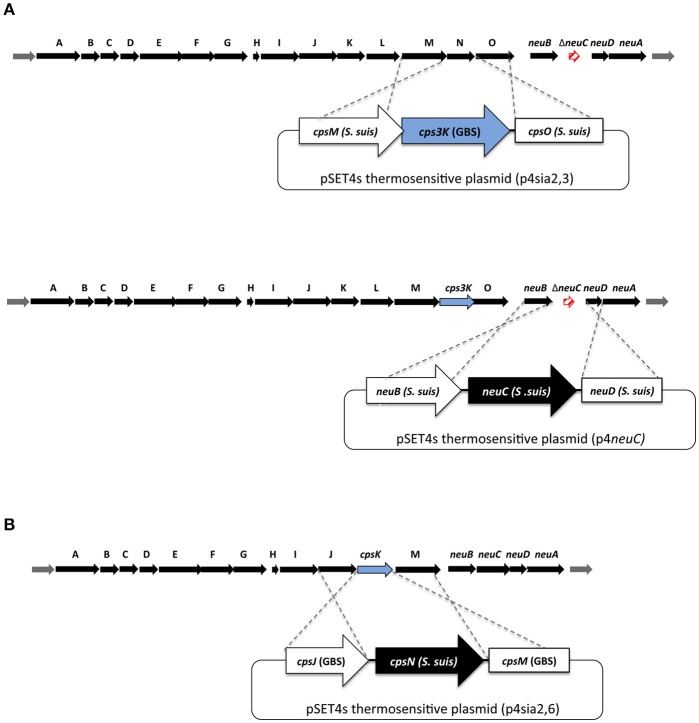
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of mutagenesis procedures to obtain sialyltransferase substitution mutants in (A) S. suis and (B) Group B Streptococcus (GBS). (A; top part) Non-lethal mutation in neuC (Δsynth) was used first to abolish capsular polysaccharide (CPS) production. Gene substitution plasmids p4sia2,3_2 and p4sia2,3_14 were introduced into S. suis SS2Δsynth (serotype 2) and SS14Δsynth (serotype 14) mutants, respectively. (A; bottom part) In order to reintroduce a functional neuC gene into SS2Δneu2C/cps3K and SS14Δneu14C/cps3K mutants, the p4neuC plasmid was introduced into SS2Δneu2C/cps3K and SS14Δneu14C/cps3K mutants to obtain indirect substitution mutants SS2sia2,3 and SS14sia2,3. (B) In order to substitute GBS type III and V sialyltransferases, direct gene replacement by double-crossover homologous recombination system was used by introducing mutation plasmids p4sia2,6_III and p4sia2,6_V.