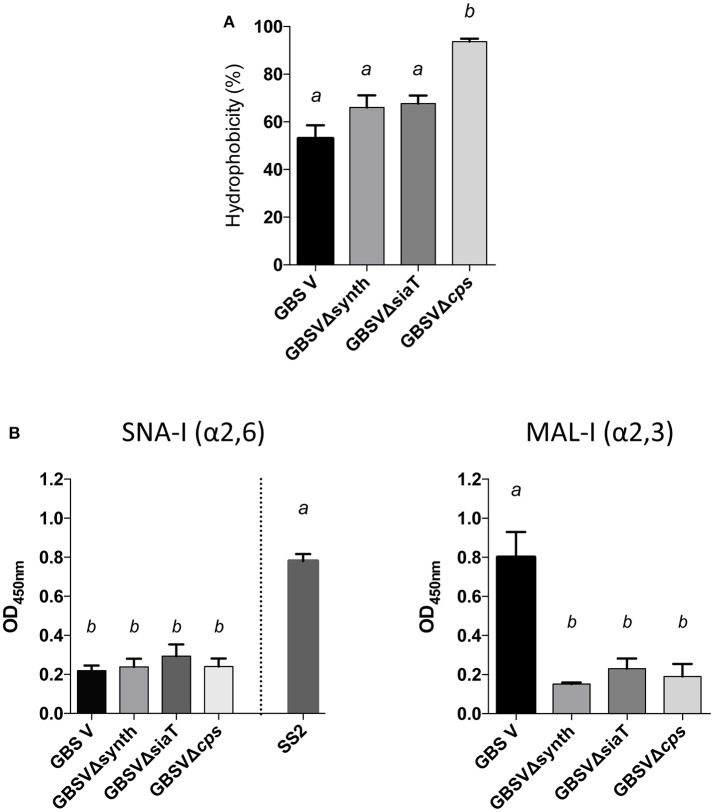
Figure 7.
Capsular polysaccharide (CPS) expression levels and recognition of specific CPS sialic acid linkage in GBS type V isogenic mutants. (A) Hydrophobicity (%) of the wild-type GBS serotype V strain (GBS V), and the sialic acid synthesis GBSVΔsynth (Δneu5B) and sialyltransferase GBSVΔsiaT (Δcps5K) deficient mutants. The non-encapsulated strain (GBSVΔcps) was used as control. (B) Whole-bacterial cell enzyme-linked lectin assay (ELLA) was performed to detect α-2,3 or α-2,6 capsular sialic acid linkage in these mutant strains. Whole bacteria were incubated with Sambucus nigra agglutinin (SNA-I) specific for Neu5Ac α-2,6 linkages, or Maackia amurensis leukoagglutinin (MAL-I) specific for Neu5Ac α-2,3 linkages. The non-encapsulated mutant GBSVΔcps was used as negative control. S. suis serotype 2 (SS2) was used as positive control for SNA-I and wild-type GBS type V as positive control for MAL-I. Data in (A,B) are expressed as mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. Student's t-test analyses reported significant differences between “a” and “b” (P < 0.05).