FIGURE 1.
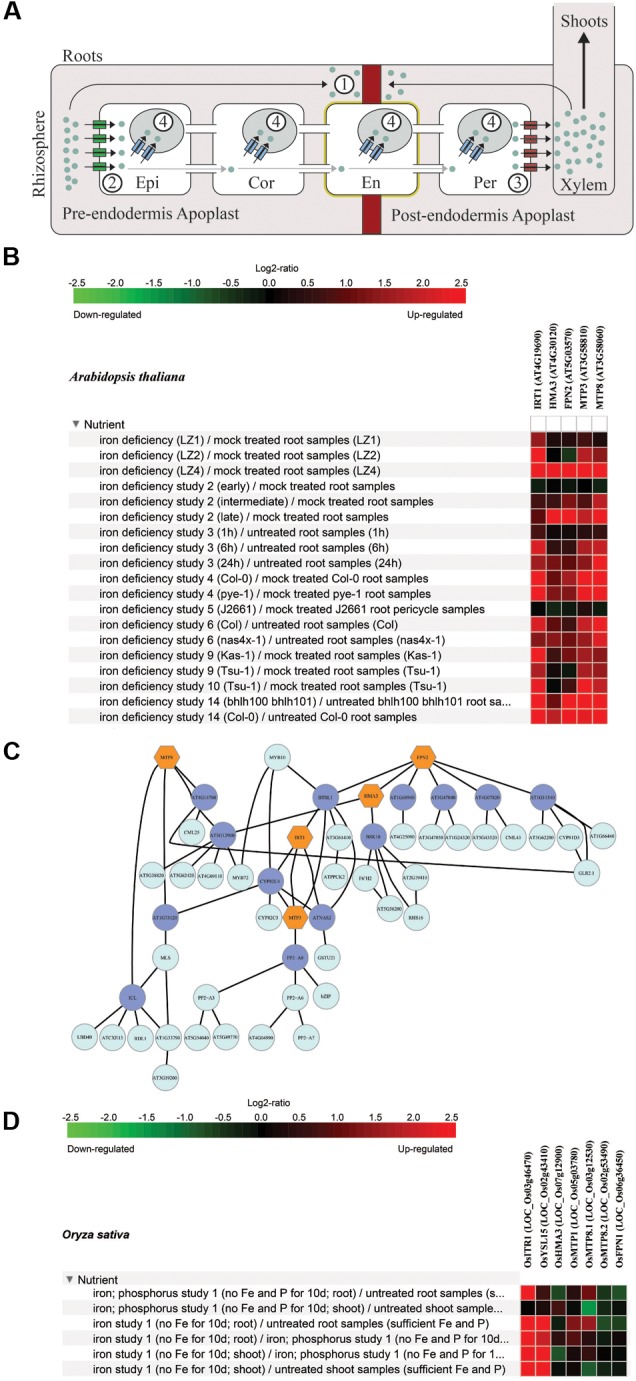
Root vacuolar compartmentalization regulating the ionome. (A) Checkpoints of ion radial movement within roots. (1) Endodermal diffusion barriers block ions entry in the apoplast connected to the xylem. (2) Influx and (3) efflux transporters control ion concentration in the root symplast. Influx and efflux transporters may also be present in plasma membranes of other cells, but are shown in epidermis and pericycle for clarity. (4) Root vacuoles can restrict symplastic movement of ions, and therefore decrease or increase their availability for xylem loading and shoot/seed translocation. Different cell layers may have distinct vacuolar repertoire for storage. Gray arrows indicate diffusion within the symplast through plasmodesmata. Epi, epidermis; Cor, cortex; En, endodermis; Per, pericycle. Red band – Casparian Strip; yellow = suberin deposition. (B) Data from Genevestigator showing regulation under Fe deficiency of Arabidopsis genes AtIRT1 (AT4G19690), AtHMA3 (AT4G30120), AtFPN2 (At5G03570), AtMTP3 (AT3G58810), and AtMTP8 (AT3G58060). (C) Graphical visualization of the coexpressed gene network of the same genes as in (B) using ATTED-II (http://atted.jp/). Nodes (hexagons and circles) represent genes, while straight lines represent coexpression. Nodes in hexagonal shape and orange color represent genes of interest. Nodes in circle shape and purple color represent genes within the network which are directly connected to the genes of interest. Nodes in circle shape and light blue color represent genes which are connected to the purple circle genes. (D) Data from Genevestigator showing regulation under Fe deficiency of rice genes LOC_Os03g46470 (OsIRT1), LOC_Os02g43410 (OsYSL15), LOC_Os07g12900 (OsHMA3), LOC_Os05g03780 (OsMTP1), LOC_Os03g12530 (OsMTP8.1), LOC_Os02g53490 (OsMTP8.2), and LOC_Os06g36450 (not yet characterized, but most similar gene to AtFPN1/AtFPN2; named OsFPN1).
