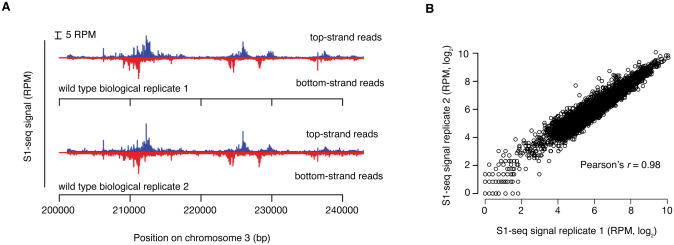
Figure 2.
Reproducibility of S1-seq: A. Spatial reproducibility of S1-seq maps. Uniquely mapped S1-seq reads were normalized to reads per million (RPM). A region of chromosome III is shown as an example of the reproducibility between two wild-type datasets. B. Quantitative reproducibility of S1-seq maps. Normalized, uniquely mapped reads were summed in 1-kb non-overlapping windows for two wild-type biological replicates. Reproduced from Mimitou, Yamada, & Keeney, 2017.