Fig. 6.
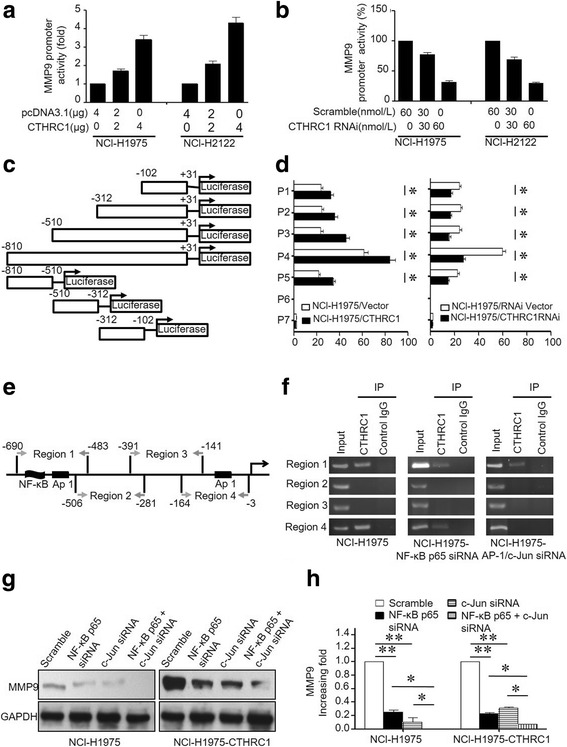
CTHRC1 transcriptionally modulates MMP9 expression through c-JUN and NF-κB signals. a CTHRC1 overexpression increased MMP9 promoter activity. b MMP9 promoter activity was inhibited when CTHRC1 was downregulated. c The promoter region was cloned as seven fragments (P1 to P7). d Transactivating activity of CTHRC1 on serial MMP9 promoter fragments as indicated in NCI-H1975 cells. CTHRC1 overexpression enhanced the promoter activity in P1–5, while CTHRC1 knockdown weakened promoter activity in P1–5. e Schematic illustration showing the PCR-amplified fragments of the MMP9 promoter. f Regions of the MMP9 promoter that were physically associated with CTHRC1 were analysed in a ChIP assay. IgG was used as a negative control. PCR amplification indicated the binding efficiencies to region 1 and region 4 were decreased in NCI-H1975-AP-1/c-Jun siRNA cells, and binding efficiency to region 1 was significantly decreased in NCI-H1975-NF-κB siRNA cells. g Western blotting revealed upregulated MMP9 expression accompanying the ectopic overexpression of CTHRC1; this MMP9 upregulation was abolished when either NF-κB or c-JUN was knocked down. Knockdown of NF-κB and c-JUN together further decreased MMP9 expression. Representative bands are shown. h The western blot results were semi-quantified and are shown in bar graph form. Experiments had been repeated 3 times. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01
