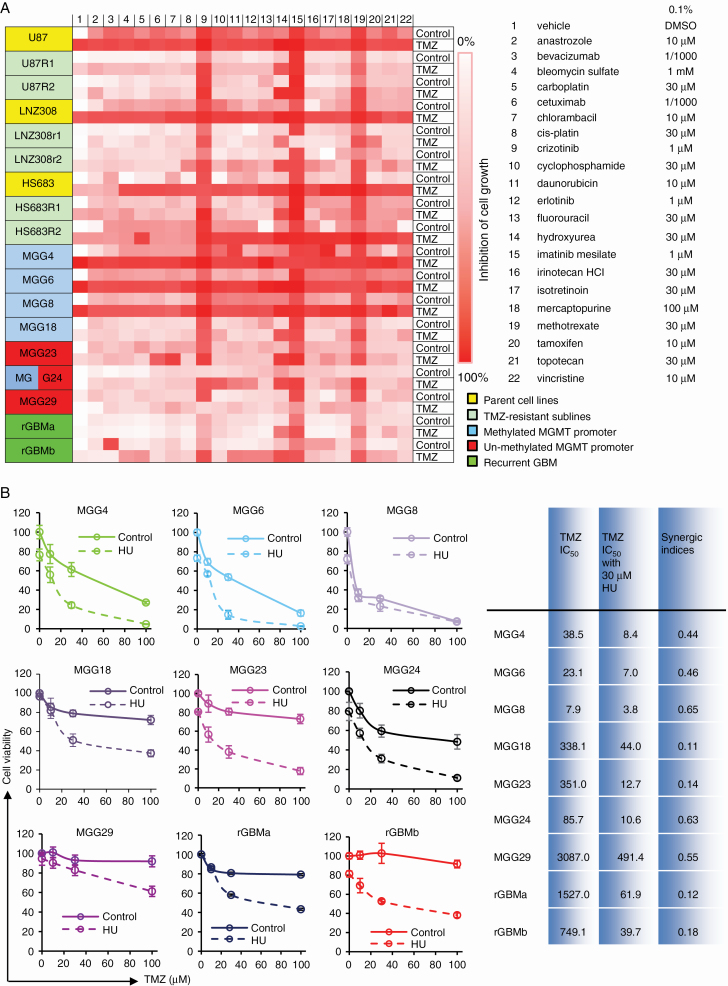
Fig. 1.
HU, identified through repurposing drug screening, restores TMZ sensitivity in resistant GBM cells in culture. (A) Heatmap from the “repurposing/recycling” chemical screen demonstrating the sensitivity of 18 GBM cell cultures to TMZ in the presence of one of the 21 most commonly prescribed chemotherapy drugs; parental cell lines U87, LNZ308, and Hs683 and 2 corresponding TMZ-resistant sublines (R1 and R2), patient-derived cells from newly diagnosed (MGG4, MGG6, MGG8, MGG13, MGG23, MGG24, MGG29) and recurrent GBM tumors (rGBMa and rGBMb). The relative decrease in cell viability at 72 h posttreatment is shown as gradations of red to white; red, no cell alive; white, same proportion of live cells as in vehicle control (0.1% DMSO). (B) All 9 patient-derived cultures were treated with different concentrations of TMZ (100 nM to 1 mM) in the presence or absence of 30 μM HU. Cell viability was measured 3 days later using the Gluc assay and normalized to the vehicle control (0.1% DMSO), which was set at 100%. Results are shown as the mean ± SD of 8 wells. Nonlinear regression of the data was performed to calculate the IC50 and the synergic indices.