Figure 3.
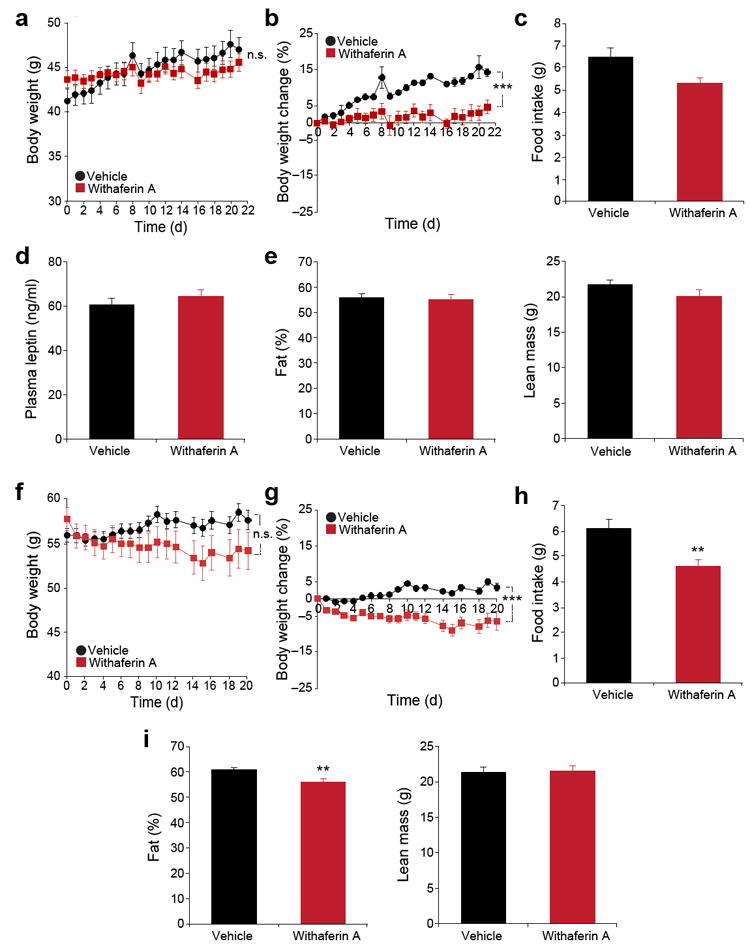
Leptin signaling-deficient mice are resistant to the weight reducing effect of withaferin A. (a–e) db/db mice received vehicle or withaferin A (1.25 mg/kg) for 21 d. (a) Body weight and (b) percent change in bodyweight during the treatment (n = 10, vehicle; n = 8, withaferin A). The experiments in a,b were repeated in seven cohorts (total n = 53, vehicle; n = 47, withaferin A). (c) Daily food intake during the first week treatment. (d) Plasma leptin concentrations after 3-week treatment period (n = 10, vehicle; n = 7, withaferin A). (e) Fat percentage (left) and lean mass (right) after 21-d treatment (n = 10, vehicle; n = 9, withaferin A). (f–i) ob/ob mice received vehicle or withaferin A (1.25 mg/kg) for 20 d. (f) Body weight and (g) percent change in bodyweight (n = 10 per group). The experiments in f,g were repeated in three cohorts (total n = 29, vehicle; n = 22, withaferin A). (h) Daily food intake during the first week treatment. (i) Fat percentage (left) and lean mass (right) of ob/ob mice after 20 d of treatment (n = 10 per group). Values are averages ± s.e.m. P values are determined two-way ANOVA (a,b,f,g) or by Student’s t test (c,d,e,h,i). ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001. n.s.; not significant.
