Figure 6.
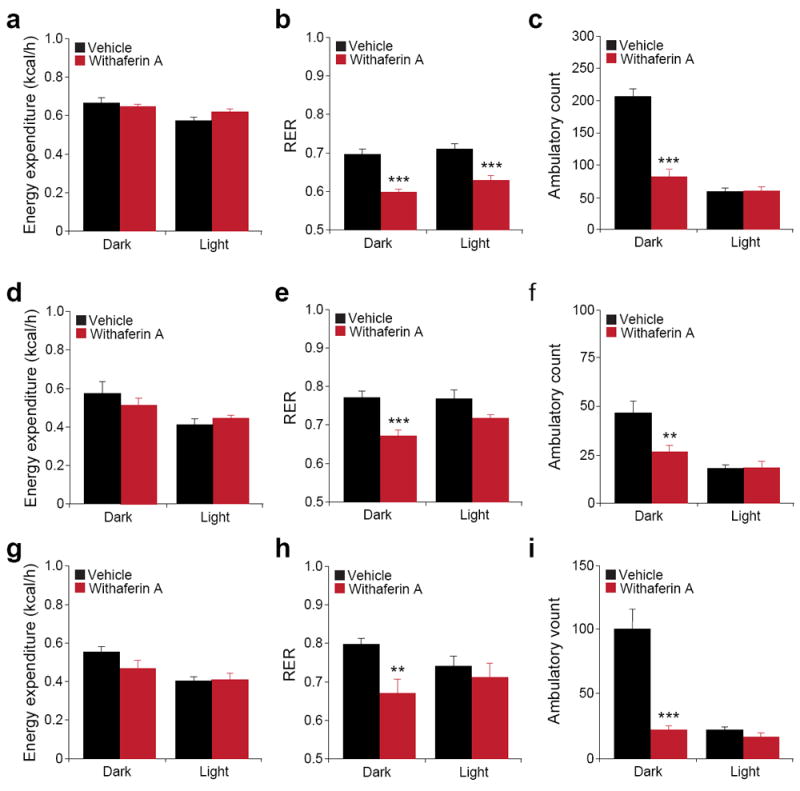
Withaferin A’s beneficial effect on metabolic homeostasis. Individually caged (a–c) DIO (total n = 16 per group from two cohorts), (d–e) ob/ob (n = 5 per group) and (g–i) db/db mice (n = 6 per group) were placed in metabolic cages and received vehicle or withaferin A (1.5 mg/kg) for 3 d. Energy expenditure (kcal/h) of (a) DIO, (d) ob/ob and (g) db/db mice. Respiratory exchange ratios (RER) (VCO2/VO2) of (b) DIO, (e) ob/ob and (h) db/db mice. Ambulatory physical activity of (c) DIO, (f) ob/ob and (i) db/db mice. Bar graphs represent average of two dark (24–36 h and 48–60 h) and two light cycles (12–24 h and 36–48 h). Results in a–c are the average of two independent cohorts. Values are averages ± s.e.m. P values are determined by Student’s t test (a–i). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
