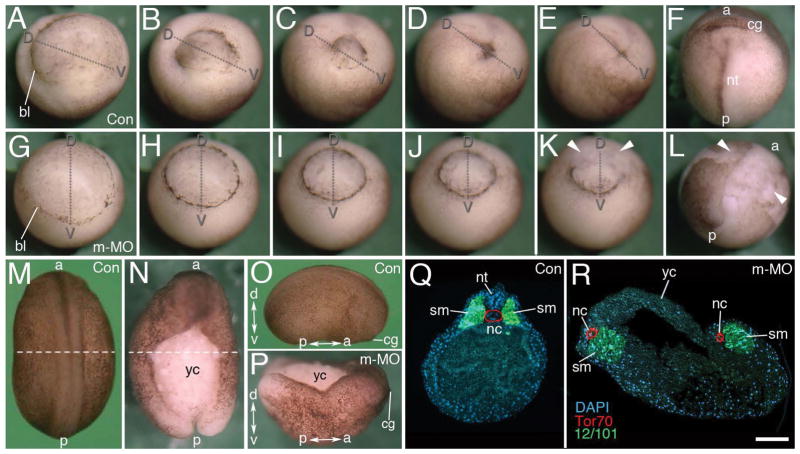
Figure 1. Maternal Mov10 is required for gastrulation and neural tube formation.
A–F) Successive time-lapse images of whole-mount control embryo undergoing normal gastrulation. G–L) Successive time-lapse images of whole-mount maternal Mov10 knockdown (m-MO) embryo that fails to complete gastrulation. Dorso-ventral and anterior-posterior axes are as labeled. White arrowheads in K and L point to yolky debris and loose cells of the blastopore and dorsal lip. M–P) Dorsal, whole-mount images from Control (Con) and m-MO injected embryos. M) dorsal view of stage 21 control embryo. N) Dorsal view of sibling m-MO injected embryo. Note large opening with exposed yolky mass of cells on the dorsal surface. The loose yolky debris has washed away from this hatched embryo. O) Lateral view of a Con embryo like that shown in M. P) Dorsal view from anterior end of m-MO injected embryo showing the “boat-shaped” phenotype. The dotted lines in M and N show the plane of sections for Q and R, respectively. Q) Section through a stage 21 control embryo showing a single notochord and two rows of somites united along the dorsal midline. Antibody to Tor70 recognizes notochord cells (in red); Antibody 12/101 recognizes somitic mesoderm (in green); DAPI in blue R) Section through a typical m-MO embryo showing failure to complete gastrulation and neurulation. This embryo has two separated files of notochord and somitic mesoderm. The dorsal side is located towards the top in Q and R. a, anterior; bl, blastopore lip; cg, cement gland; d, dorsal; nt, neural tube; nc, notochord; nt, neural tube; p, posterior; sm, somite; v, ventral; yc, yolk cells. Scale bar in R equals 120μm (for A–L), 450μm (for M–N), 440μm (for O–P), and 80μm (for Q–R).