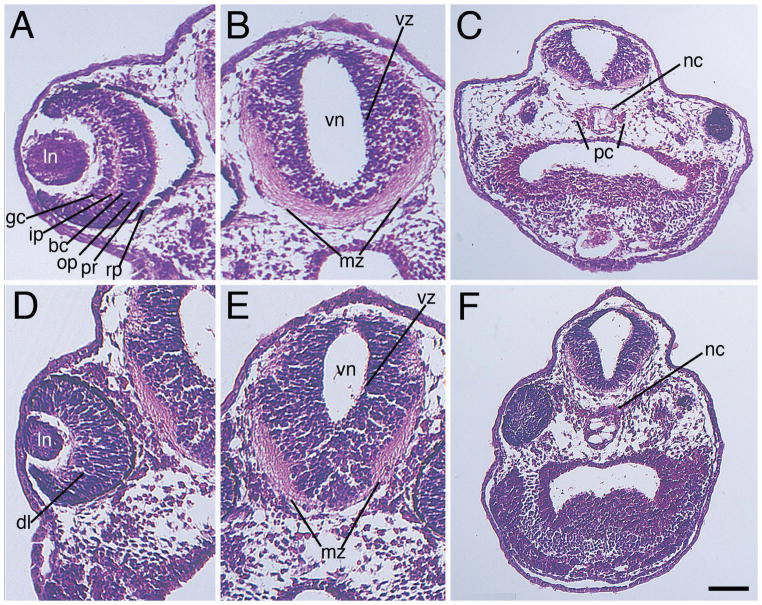
Figure 6. Knockout of zygotic Mov10 leads to defects in the eye and brain structure.
A–C) Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of control (Con) morpholino injected embryos, as labeled. A) Representative section of a control eye showing distinct, well-organized layers of the retina in a control embryo, as labeled. B) Forebrain region displaying a well-developed ventricular zone and marginal zone. Note large mass of axonal fibers within the ventral marginal zone. C) Lower magnification image showing the notochord and parachordal cartilage (D–F) Hematoxylin and Eosin stain of z-MO injected embryos. D) Section reveals a smaller eye with disorganized retinal layers. E) Section of the brain with a reduced marginal zone area. Note a reduced mass of axonal fibers within the ventral marginal zone. F) Lower magnification image revealing an enlarged notochord and no distinguishable parachordal cartilage. Dorsal is located towards the top of these images. bc, bipolar cell layer; dl, disorganized layers; gc, ganglion cell layer; ip, inner plexiform layer; mz, marginal zone; nc, notochord; op, outer plexiform layer; pc, parachordal cartilage; pr, photoreceptor; rp, retinal pigment epithelium; vz, ventricular zone. Scale bar in F equals 100μm (for A–B and D–E), and 170μm (for C and F).