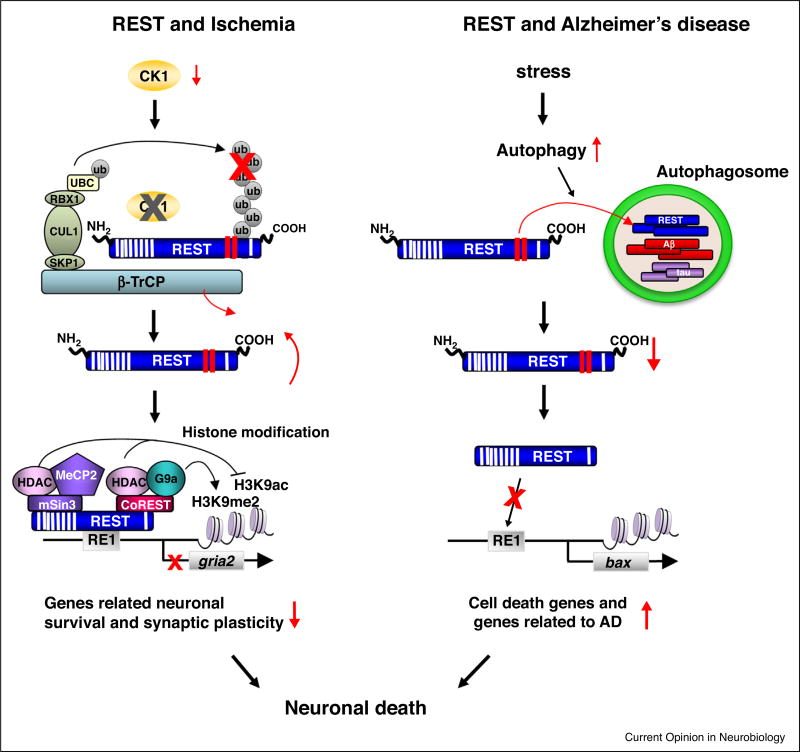
Figure 1.
Regulation of REST in global ischemia and AD. Left, global ischemia reduces abundance of CK1 and E3 ligase β-TrCP, resulting in an increase in REST in the hippocampal CA1. REST binds to the RE1 element within the promoter of target genes such as gria2 and orchestrates the assembly of mSin3A and CoREST, HDACs 1 and 2, G9a and MeCP2. The REST-corepressor complex promotes epigenetic remodeling of core histone proteins at the promoter of target genes and represses transcription of genes important to synaptic plasticity and neuronal survival. Right, In AD brains oxidative stress activates autophagy and formation of autophagosome. REST is engulfed in autophagosomes, together with misfolded proteins, such as Aβ and tau, which, in turn, reduces REST abundance in the nucleus. Loss of REST in the nucleus causes an increase in expression of genes involved in neuronal death and AD pathology.