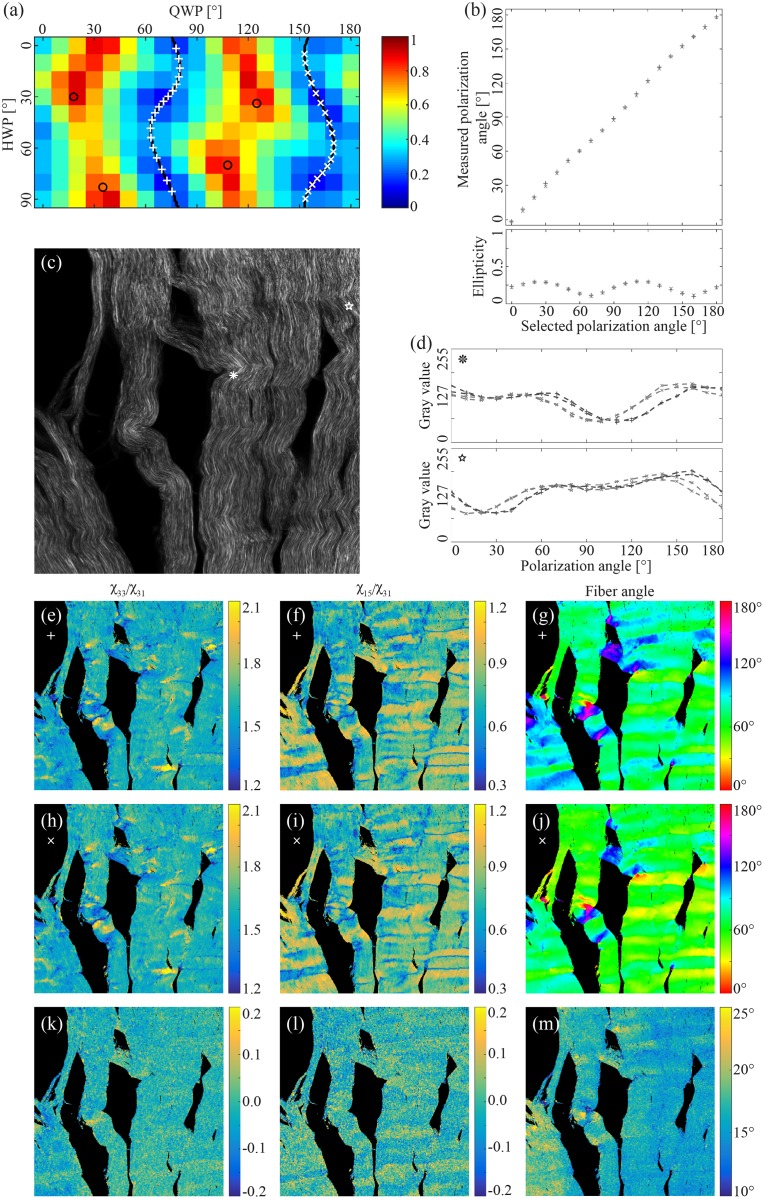
Fig 6.
Waveplate combinations that provide linear polarization were selected at polarization angle intervals of 10° from 0° to 180° (a, white crosses and plus signs). There are two different combinations that provide the same polarization angle, thereof the two separate sets (crosses vs plus signs). The polarization angle and ellipticity were measured for all waveplate combinations in both sets (b). Tendon was imaged twice using all waveplate combinations (c, average). Two pixels were selected (c, white asterisk and star) to demonstrate the variation of the intensity as a function of polarization angle for the two sets (d). The second order susceptibility tensor ratios and fiber angle were calculated separately for the two sets (plus signs: e, f, g, crosses: h, i, j). The difference between the two was emphasized by taking subtracting the results from one of the sets (crosses) from the other (plus signs) (k, l, m).