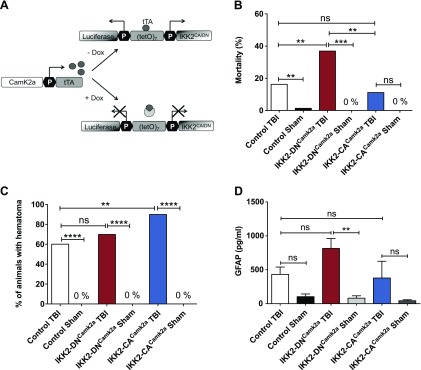
Figure 1.
Immediate consequences of CHI on mice with modulated neuronal NF-κB activity. A) Generation of conditional transgenic IKK2-DNCamk2a and IKK2-CACamk2a mouse models using the tetracycline-regulated gene-expression system. Expression of the IKK2-DN (loss-of-function) or IKK2-CA (gain-of-function) transgene and a luciferase reporter gene was controlled by the bidirectional tetracycline-controlled transcriptional activation (tTA)–dependent promoter (tetO7). The Camk2a.tTA module specified transgene expression to neurons with Camk2a-activity. Dox blocked transgene expression. B) Mortality of mice during CHI procedure. Immediate posttraumatic mortality rate is depicted as the percentage of animals that died. IKK2-DNCamk2a mice showed a significantly enhanced posttraumatic mortality compared to control and sham-treated animals, whereas mice with neuronal NF-κB activation (IKK2-CACamk2a) had a mortality similar to that of as control mice. (Control TBI, n = 115; Control Sham-Treated, n = 62; IKK2-DNCamk2a TBI, n = 78; IKK2-DNCamk2a Sham, n = 21; IKK2-CACamk2a TBI, n = 35; IKK2-CACamk2a Sham, n = 20). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 [not significant (ns), by Fisher’s exact test]. C) Quantification of hematoma formation in IKK2-DNCamk2a, IKK2-CACamk2a, and control mice after TBI. CHI induced similar distributed hematoma formation in control and IKK2-DNCamk2a animals. IKK2-CACamk2a mice were slightly more prone to hematoma development than controls. (Control TBI, n = 76; Control Sham, n = 51; IKK2-DNCamk2a TBI, n = 37; IKK2-DNCamk2a Sham, n = 18; IKK2-CACamk2a TBI, n = 31; IKK2-CACamk2a Sham, n = 20). **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 (ns, by Fisher’s exact test). D) Plasma levels of GFAP after CHI. IKK2-DNCamk2a mice showed elevated levels of GFAP in the plasma 6 h after TBI. Means ± sem (n = 6–12). **P < 0.01 (ns, by 1-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test).