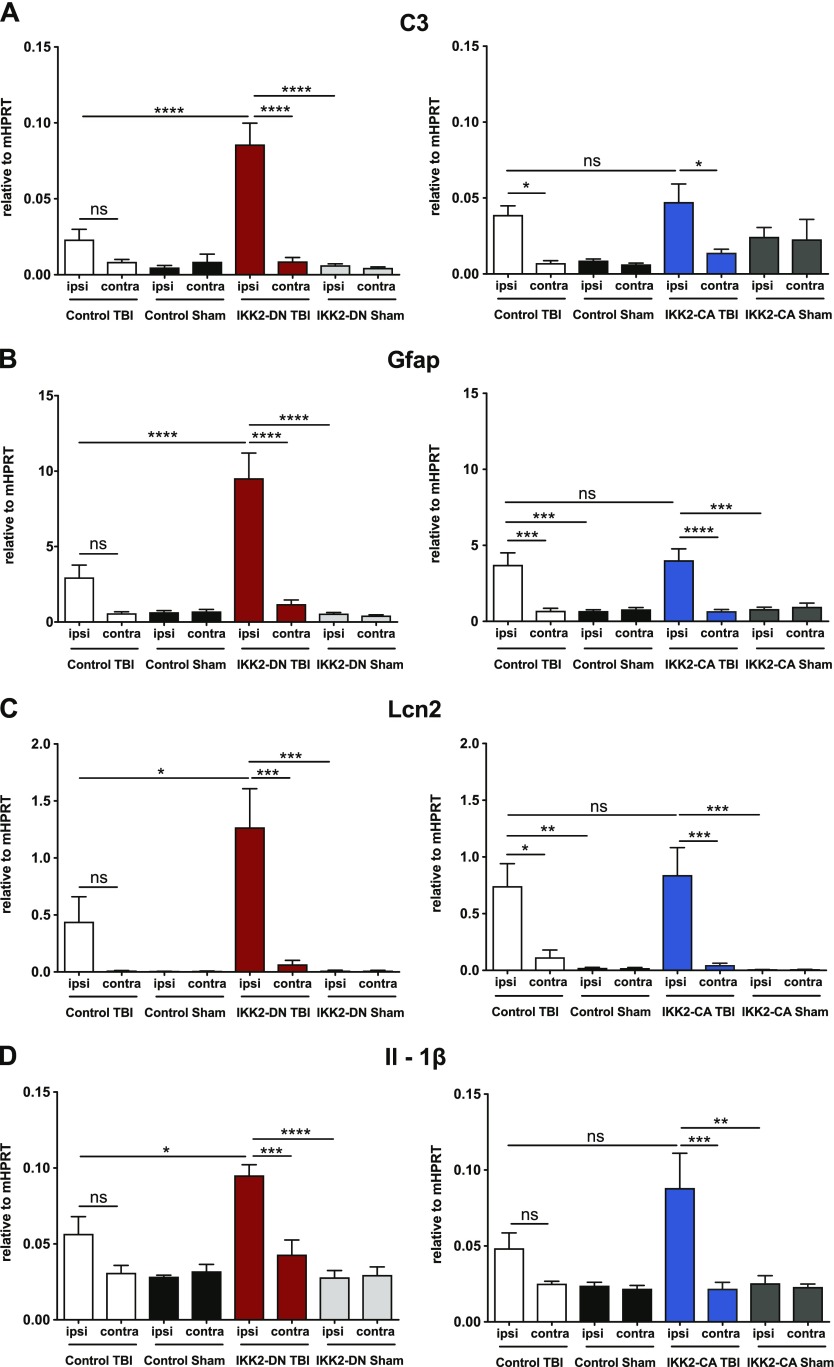
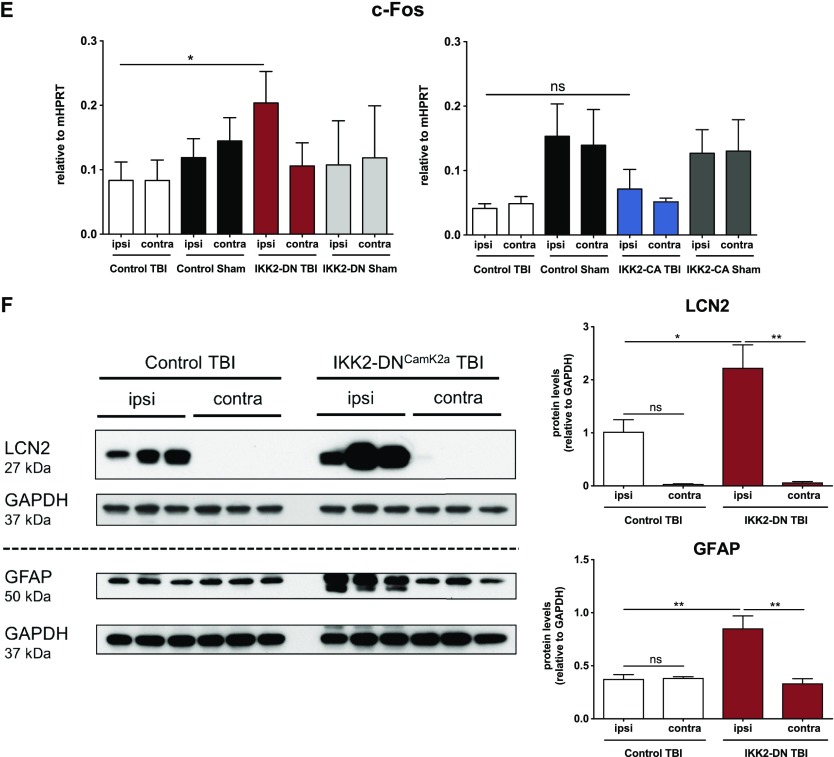
Figure 4.
IKK2-DNCamk2a mice exhibit prominent up-regulation of neuroinflammatory factors after trauma. A–E) Expression of proinflammatory genes 3 d after TBI. Most proinflammatory factors were significantly up-regulated in the cortical impact area of IKK2-DNCamk2a mice, but not in IKK2-CACamk2a mice vs. control littermates. These factors include the complement factor C3 (A), the astroglial marker Gfap (B), the acute phase protein Lcn2 (C), the inflammatory cytokine Il1b (D), and the neuronal activity marker c-Fos (E). Expression levels measured by qPCR are presented relative to Hprt. Means ± sem (n = 4–6). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 [not significant (ns), 3 d after TBI between indicated groups, by 1-way-ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test]. F) Expression of astroglial and acute phase proteins after trauma. Representative immunoblot analysis and quantification of LCN2 and GFAP protein levels in brain lysates of 12-wk-old control and IKK2-DNCamk2a mice 3 d after CHI. GAPDH was the loading control. Means ± sem (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (by 1-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test).