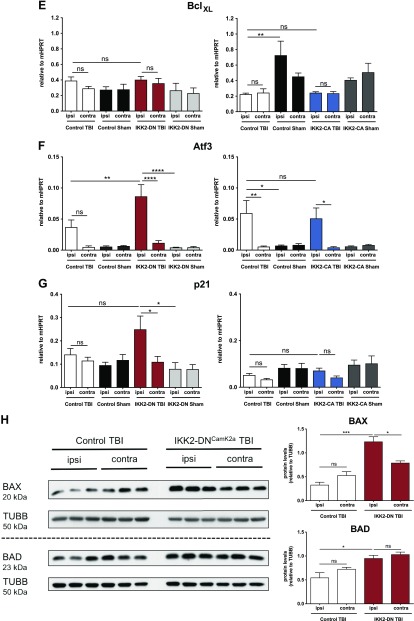
Figure 5.
Neuronal NF-κB inhibition leads to up-regulation of proapoptotic factors after CHI. A–G) Expression of genes regulating apoptosis 3 d after TBI. Proapoptotic, but not antiapoptotic, factors were significantly elevated in the cortical impact area of IKK2-DNCamk2a mice, but not in IKK2-CACamk2a mice vs. control littermates. qPCR analysis of the proapoptotic genes Bax (A), Bad (B), and Bak (C); the antiapoptotic genes Bcl2 (D) and BclXL (E); and the stress response genes in the p53 pathway Atf3 (F) and p21 (G). Expression levels measured by qPCR are presented relative to Hprt. Means ± sem (n = 4–6). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 [not significant (ns), at 3 d TBI between the indicated groups, by 1-way-ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test]. H) Expression of proapoptotic proteins after trauma. Representative immunoblot analysis and quantification of BAX and BAD protein levels in brain lysates of 12-wk-old control and IKK2-DNCamk2a mice. TUBB is used as loading control. Means ± sem (n = 3). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 (ns, 3 d after CHI, between the indicated groups, by 1-way-ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test).