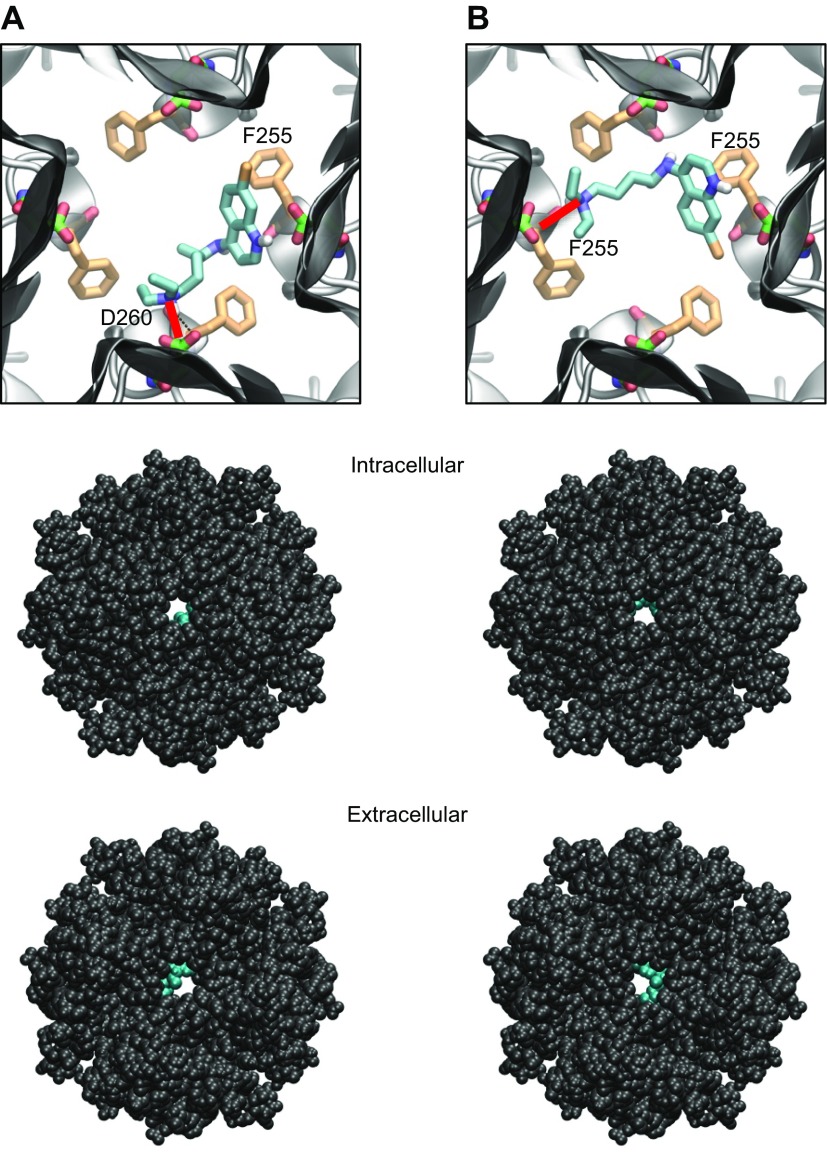
Figure 4.
Docking of chloroquine in the ion-permeation pathway of the Kir3.1 channel. A, B) Two lowest energy poses. Top: magnified view of the binding poses of chloroquine (cyan sticks) in Kir3.1. The D260 and F255 residues from each of the 4 Kir3.1 subunits are shown in green and orange sticks, respectively. A) The amine nitrogen of chloroquine forms a hydrogen bond (red line) with the side chain of D260 in 1 subunit, whereas the aminoquinoline ring of chloroquine is involved in an aromatic–aromatic interaction with the phenylalanine ring of F255 in the adjacent subunit. B) The amine nitrogen of chloroquine hydrogen bonds (red line) the carbonyl oxygen of F255 in 1 subunit, whereas the aminoquinoline ring of chloroquine is involved in an aromatic–aromatic interaction with the phenylalanine ring of F255 in the opposing subunit. Middle, bottom: van der Waals representations of the channel bound to chloroquine (cyan), viewed from the intracellular and extracellular sides, respectively.