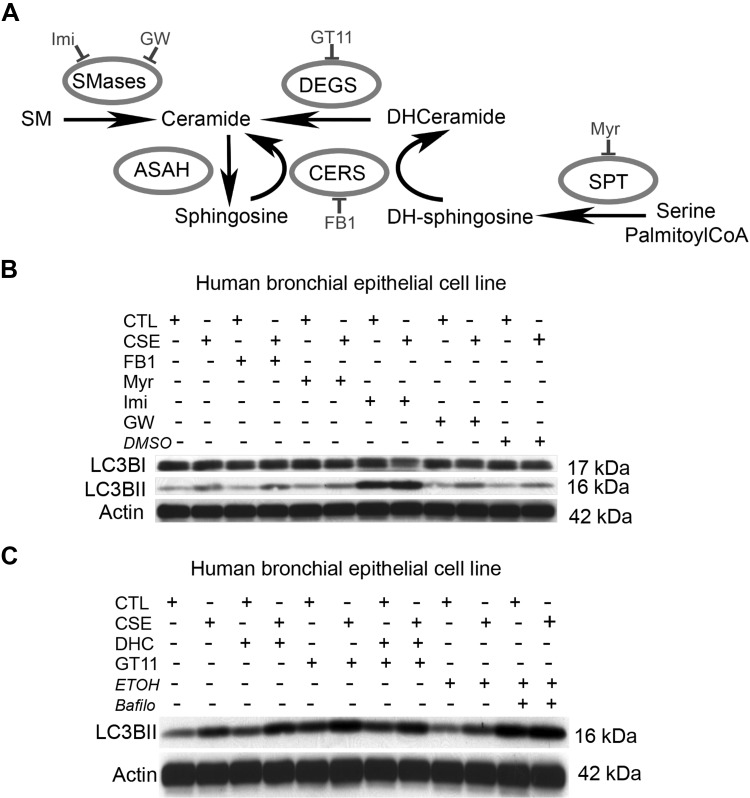
Figure 3.
Effect of Cer synthesis inhibition on LC3BII abundance during CS exposure. A) Schematic of Cer synthesis via sphingomyelin (SM) hydrolysis catalyzed by sphingomyelinases (SMases); de novo synthesis from serine and C16 coenzyme A (CoA), catalyzed by the serial action of serine C16 transferase (SPT), CerS, and DEGS; and via the recycling pathway, which uses sphingosine produced from Cer hydrolysis by ceramidases (ASAH) to resynthesize Cer via CERS. Noted are pharmacological inhibitors used to target enzymes involved in Cer production. DH, Dihydro; GW, GW4869; Imi, Imipramine. B, C) Representative immunoblots (n = 3) of LC3B and the loading control actin in cells exposed to ctl or CSE (2% CSE for 3 h; n = 3), while treated with inhibitors of Cer synthesis, DHC, or vehicle controls [DMSO and ethanol (ETOH)] or the lysosomal inhibitor bafilomycin (Bafilo) as a positive control for LC3BII accumulation. Note that increased LC3BII in response to CSE is enhanced by Imi (ASM inhibitor) and modestly decreased by Myr (SPT inhibitor); also, note that either exogenous DHC exposure or inhibition of endogenous DHC metabolism (GT11) increased LC3BII, even in ctl cells.