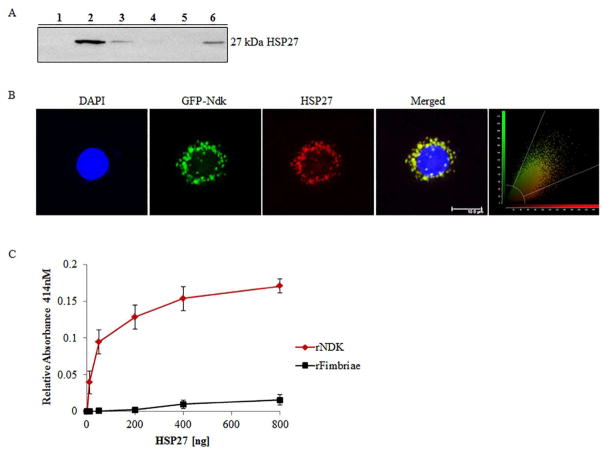
Figure 1. HSP27 binds P. gingivalis Ndk in primary GECs.
(A) Western blot analysis of the presence of HSP27 in the eluent of a GST-pull down of rNdk incubated with primary GEC cytosolic lysate. Lane Designations: 1) Negative control – GST-resin with GEC cell lysate only; 2) GST-resin, P. gingivalis NDK, and GEC cell lysate; 3) Prey flow-through from Lane 1; 4) Prey flow-through from Lane 2; 5) Bait flow-through from Lane 2; 6) Positive control – cell lysate from GECs. (B) Representative confocal micrograph of primary GECs transfected with GFP-Ndk (green) and immunostained for HSP27 (red) with DAPI and representative confocal colocalization analysis scatterplot Zeiss; Bar 10μm. NIH Image J analysis of HSP27 and Ndk co-localization calculated Manders Coefficient as 0.92; n=21. (C) ELISA binding assay of His-tagged recombinant Ndk (rNdk immobilized on a 96-well plate and incubated with varied amounts of HSP27. Absorbance reflective of the amount of HSP27 bound was measured at 414nm. His-tagged recombinant-fimbriae of P. gingivalis were added for comparison of non-specific binding. All the assays were repeated at least in three separate experiments.