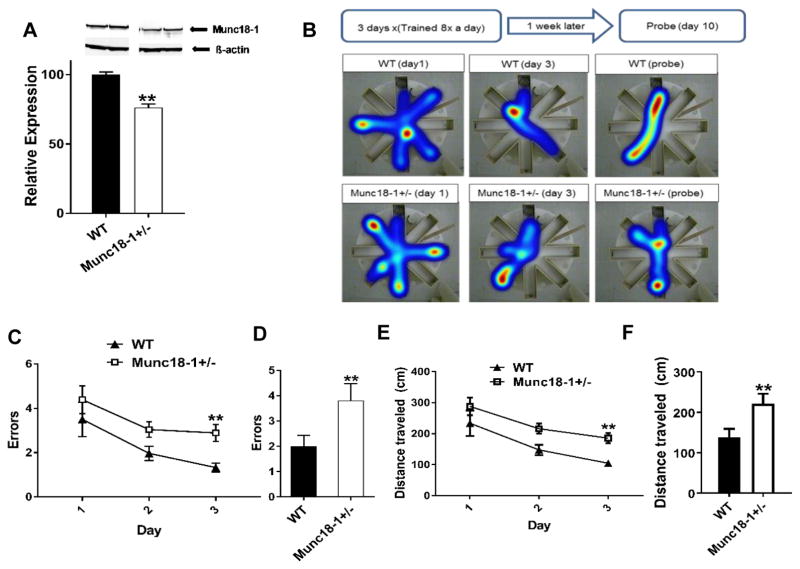
Fig. 1.
Spatial learning and memory impairment in munc18-1+/− mice. (A) Western blot data showing munc18-1+/− animals express 25% less munc18-1 than WT controls (WT= 100±1.96, n=6; munc18-1+/−= 76.30±2.57, n=7; p<0.0001). (B) Illustration of experimental procedure and representative heat map data of WT and munc18-1+/− mice in the RAWM. (C) Graph depicts errors made during acquisition phase. Munc18-1+/− animals make significantly more errors (# of entries into the incorrect arm) by day 3 (2.9±0.4) of the acquisition when compared to WT animals (1.3±0.2) and (D) bar graph depicts that on the probe day, munc18-1+/− animals again performed with more errors (3.8±0.7) when compared to WT animals (2±0.4). (E) Munc18-1+/− animals covered more distance by day 3 (munc18-1+/−= 185.7 ± 17.1 cm; WT= 104.7 ± 9.2 cm) and (F) also on the probe day (munc18-1+/−= 221.3 ± 24.8 cm; WT= 138.2 ± 21.1 cm) compared to WT controls. (WT n=8, munc18-1+/− n=9 mice; p=0.007 using 2-way RM ANOVA.