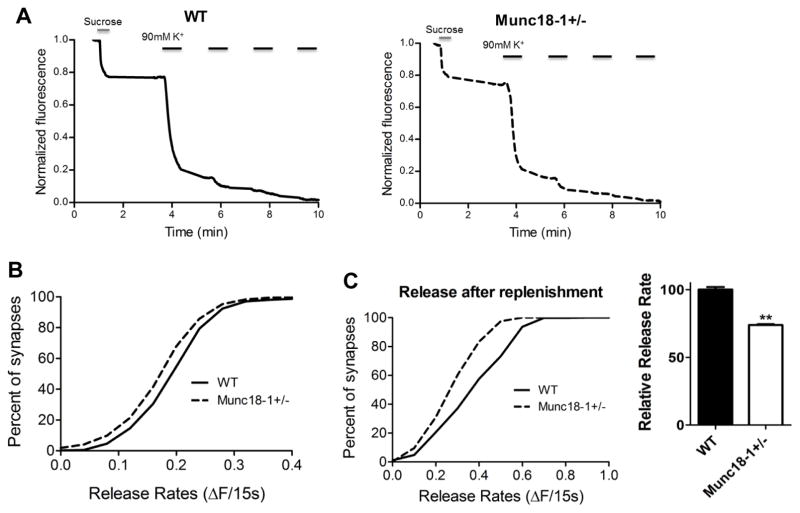
Fig. 5.
Decreased readily releasable pool (RRP) of synaptic vesicles in munc18+/− mice. (A) Representative traces of fluorescence loss during the procedure. High sucrose Tyrode solution is used to drive release during the first destaining. (B) Cumulative histogram showing munc18-1+/− (n=13; 1516 synapses) neurons have a smaller readily releasable pool size when compared to WT (n=5; 602 synapses) (p<0.001 Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). (C) panels depict the cumulative distribution of synaptic release during high K+ stimulation 90 seconds after sucrose application (left); bar graph reveals that munc18-1+/− neurons released approximately 26% less fluorescence than WT neurons (normalized to 100%) during that period (p<0.001, two tailed t-test)