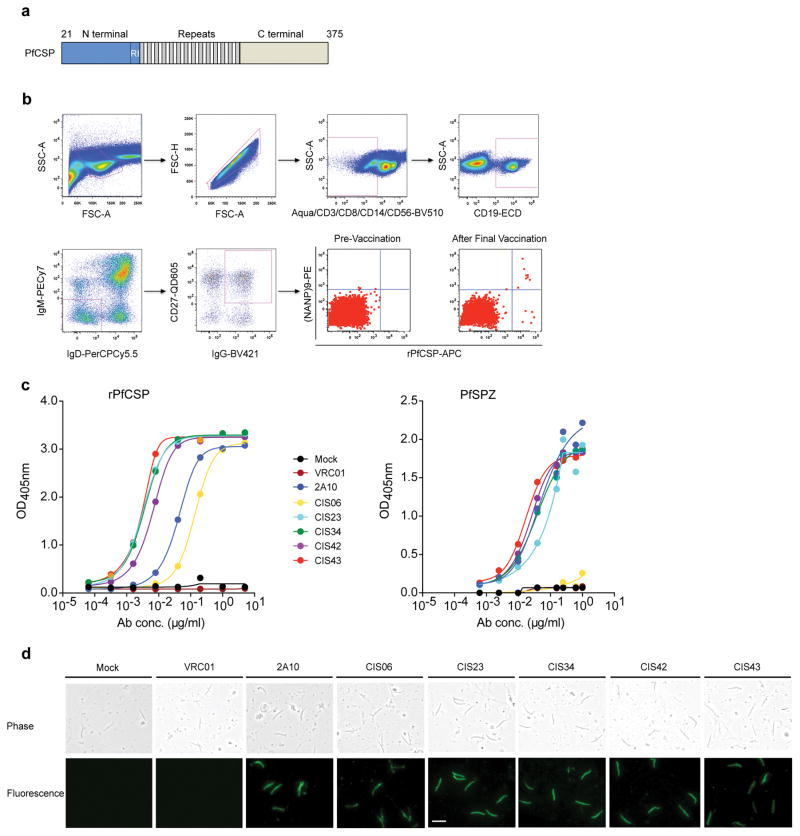
Figure 1. Isolation and binding specificity of mAbs from rPfCSP specific-memory B cells.
a, Schematic representation of rPfCSP (residues 21–375). Signal (1–21) and anchor (375–397) residues are excluded. The N-, C-terminal, and repeat domains are shown. The conserved region I (RI) is indicated. b, Gating strategy for sorting rPfCSP and (NANP)9 memory B cells. rPfCSP-specific, CD19+ IgG+ CD27+ memory B cells from pre-vaccination or after the 5th (last) vaccination. c, Binding of varying concentrations of mAbs to rPfCSP by ELISA. OD405nm, optical density at 405 nm. d, Binding of mAbs to PfSPZ by ELISA. e, Binding of mAbs to PfSPZ by immunofluorescence assay (IFA). Phase contrast and fluorescence channels are shown. Scale bar, 10 μm. In c–e, Negative controls: Mock, transfection filtrate; VRC01, a human anti-HIV-1 IgG1 isotype control mAb. Positive control: 2A10, mouse anti-PfCSP repeat mAb. Data are representative of two independent experiments (c–e).