Fig. 6. Interferon signaling responses in the STI-induced PID transcriptional signature are driven by CT infection.
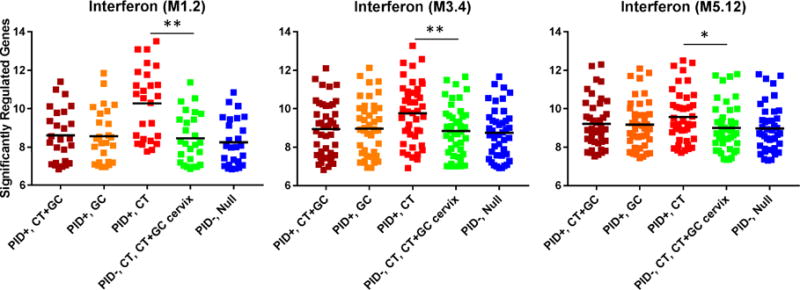
Median expression levels of interferon signaling genes among women with PID and chronic endometritis due to CT+GC, GC only, and CT only; and women without PID or endometritis with cervical infection due to CT or CT+GC, and asymptomatic uninfected women. Dots represent the median expression value for each individual transcript (log2 transformed expression) in all five subject groups in interferon modules (M1.2, M3.4, and M5.12) while the black bar indicates the group mean. Pairwise comparisons followed significant ANOVA after Bonferroni correction for all three modules. Genes related to interferon were significantly overexpressed in women with PID and chronic endometritis induced by CT alone compared to women with cervical infection due to GC or CT+GC; (p < 0.001 for M1.2, p = 0.004 for M3.4, p = 0.045 for M5.12); whereas expression levels for women with PID and chronic endometritis due to CT+GC or GC alone were not different than infected cases or uninfected controls. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
