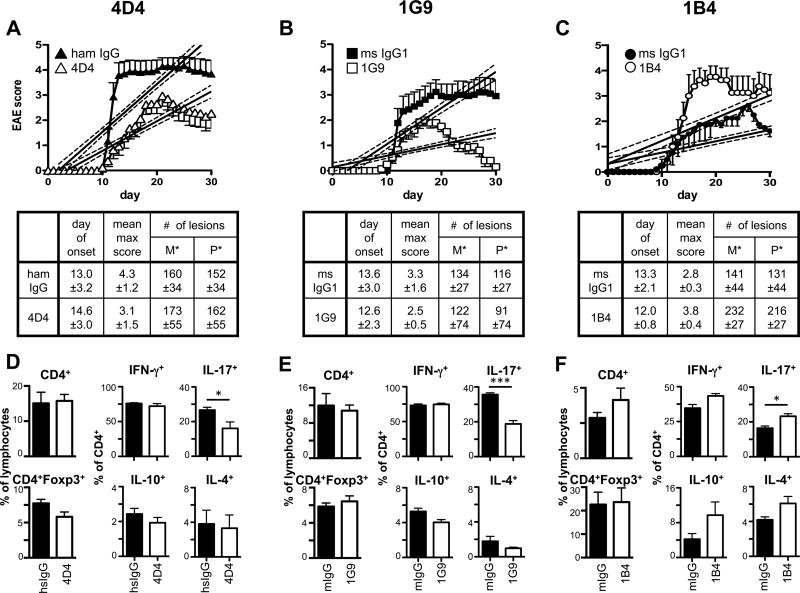
Figure 4. Functional anti-TIGIT antibodies modulate disease severity in EAE.
Wild type B6 mice were immunized s.c. with 100 µg (A, B; D, E) or 10–15µg (C; F) MOG35–55 peptide in CFA, followed by injection of 100 ng pertussis toxin i.v. on day 0 and day 2. Mice also received 100 µg anti-TIGIT (or isotype control: Armenian hamster IgG for clone 4D4 or mouse IgG1 for 1G9 and 1B4) antibody i.p on days 0, 2, 4, 10, and 17 and were monitored daily for EAE. Mean clinical score ± SEM is shown and linear regression curves of the disease for each group is depicted (the 95% confidence intervals are represented with dashed lines; combined data of 2-3 independent experiments). The number of lesions in the meninges (M*) and parenchyma (P*) were determined by histopathology when control mice were at the peak of disease (A, B: day 14; C: day 17). (D–F) At the peak of disease, CNS infiltrating cells were isolated, re-stimulated with PMA/ionomycin for 4h and analyzed for the production of IFN-γ, IL-17A, IL-10, and IL-4 by intracellular cytokine staining. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001.