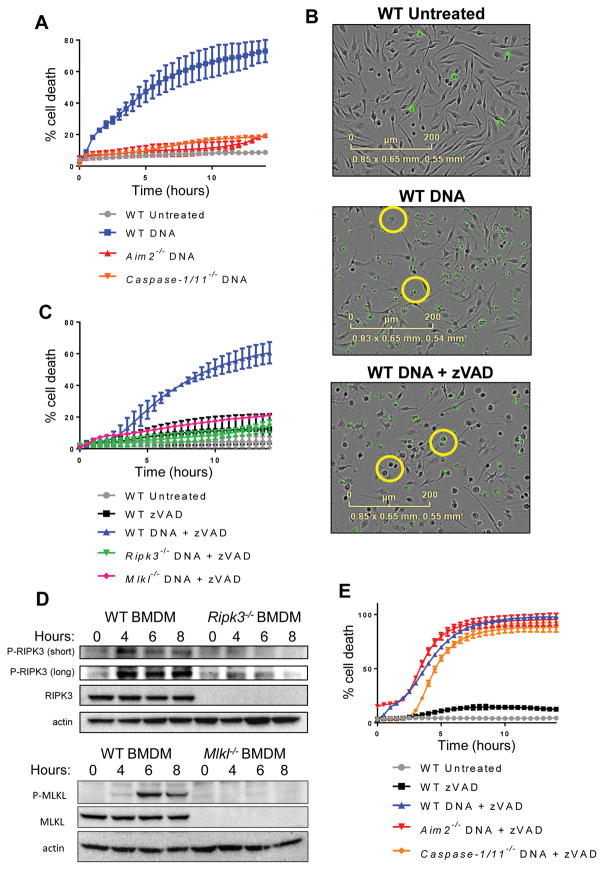
Figure 1. Introduction of DNA into the cytosol can trigger necroptotic cell death.
(A) Kinetic cell death of WT, Aim2−/−, or Caspase-1/11−/− primary bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) after transfection with 2 μg/ml DNA. Death measured by uptake of cell impermeable Sytox green dye, and normalized to starting number of cells stained with cell permeable Syto green dye to calculate percent cell death. Error bars represent SD from three independent experiments. (B) IncuCyte images of WT BMDM treated with 2 μg/ml DNA, or 2 μg/ml DNA + 50 μM zVAD. Sytox Green staining is shown in green. (C) Kinetic cell death of WT, Ripk3−/−, or Mlkl−/− BMDM after treatment with 2 μg/ml cytosolic DNA and 50 uM pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD. (D) Western blot analysis of phosphorylated RIPK3 or MLKL at short and long exposure following treatment of 5 μg/ml cytosolic DNA and 50 μM pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD in WT, Ripk3−/−, or Mlkl−/− BMDM. “z” in hours indicates zVAD alone control. (E) Kinetic cell death of WT, Aim2−/−, or Casp1/11−/− BMDM after treatment with 2 μg/ml cytosolic DNA and 50 μM pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD.