Figure 1.
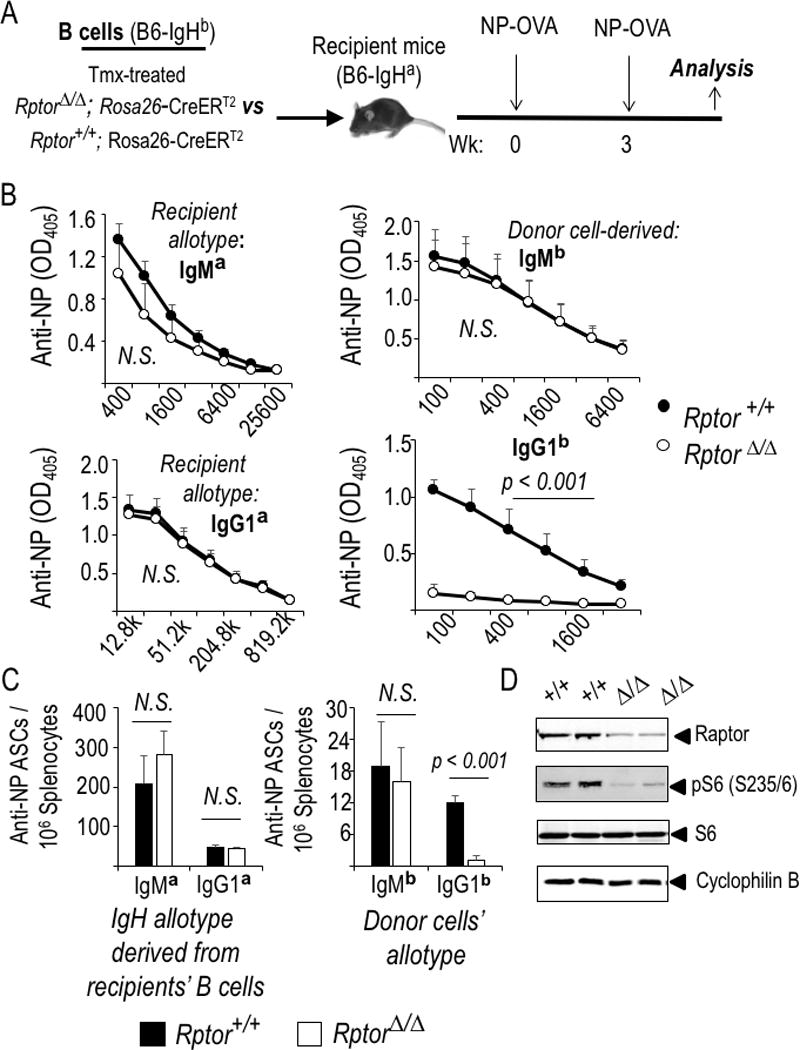
B cell-autonomous mTORC1 regulates the class switch and production of antibodies in response to NP-KLH immunization. (A) Equal numbers of B cells from tamoxifen-treated WT (Rptor +/+) or Raptor-deficient (Rptor fl/fl) CreERT2+ mice were transferred into CD45.1 (Fig. 2F, G) or IgHa-[a allotype]-disparate recipients that were then immunized following the schedule in the schematic. (B, C) Relative antibody concentrations (B), and prevalence of splenocytes that secrete Ag-specific Ab of the indicated isotype after harvesting immunized IgHa mice that received IgHb B cells (WT or Raptor-depleted, closed and open symbols, respectively) (C). (B) The mean (±SEM) data from three independent replicate experiments of Ig allotype disparate ELISA’s for all-affinity IgM/ G1a recipient antibody and IgM/G1b donor antibody responses. (C) Mean (±SEM) data from allotype-specific measurements of ASC by ELISPOT in the same three independent experiments (nine mice for each genotype of donor B cells). (D) Efficient mTORC1 inactivation via deletion of the conditional Rptor allele. Shown are immunoblots performed using the indicated Ab and extracts of B cells purified from mice of the indicated genotypes (one experiment representative of 2-3 replicates with biologically independent samples).
