Figure 5.
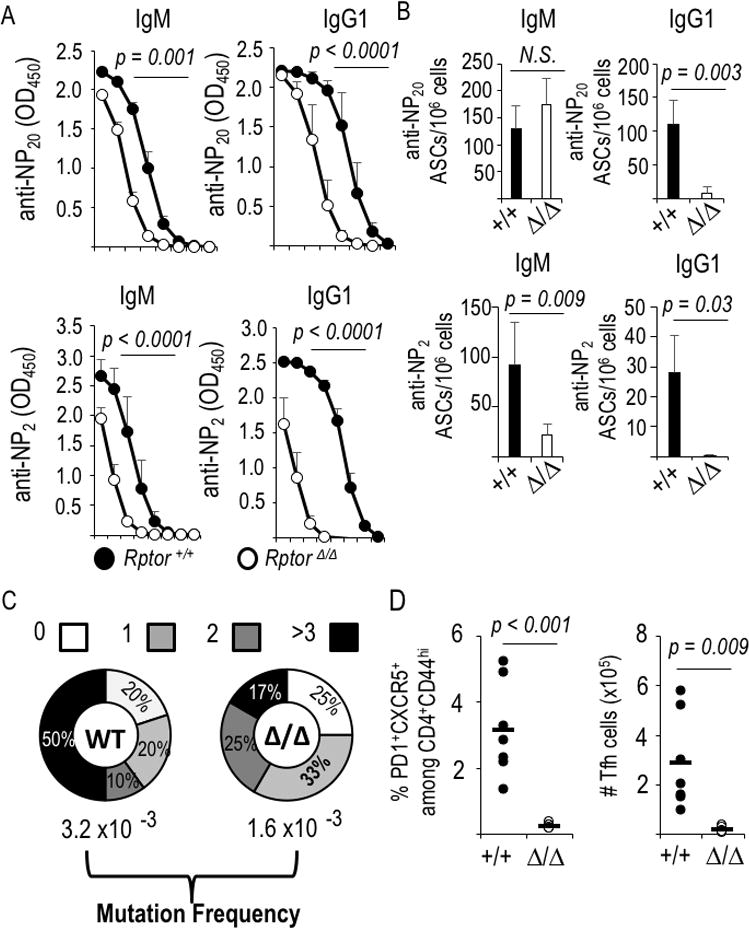
B cell-intrinsic mTORC1 promotes somatic mutation of Ig VH DNA and dramatically enhances affinity maturation. (A) All-affinity (anti-NP20) and high-affinity (anti-NP2) IgM and IgG1 in sera of immunized and boosted, tamoxifen-injected huCD20-CreERT2 mice that were either Rptor+/+ or Rptorf/f (as in Fig. 2A). Shown are the mean (±SEM) values across serial 4-fold dilutions for the independent mice (n=8, Cre+ WT; n=7 Cre+ Rptor Δ/Δ), in three separate experiments. (Initial dilutions: NP20, 1:400; NP2, 1:100). (B) Mean (±SEM) frequencies of ASCs quantified as all-affinity (anti-NP20) and high-affinity (anti-NP2) IgM- and IgG1-secreting cells in spleens of the immunized mice of Fig. 2 and Fig. 5a. (C) B cells from tamoxifen-treated CreERT2+ mice (WT and Rptor Δ/Δ) were transferred into μMT recipients that were immunized with NP-KLH. After flow purification of viable NP-binding IgDneg GL7+ B cells, rates of somatic mutation in a non-coding interval of VH186-2 of genomic DNA were scored [as in (43)]. (D) Raptor-deficient B cells fail to support the Tfh population. Splenocytes from immunized and boosted mice (as in Fig. 2A-E and Fig. 5A, B) were analyzed by flow cytometry to determine the fraction and number of Tfh (CXCR5+ PD-1+) cells among activated (CD44+) CD4+ T cells. Graphs display the values measured for each individual mouse, along with means (horizontal bars).
