Figure 7.
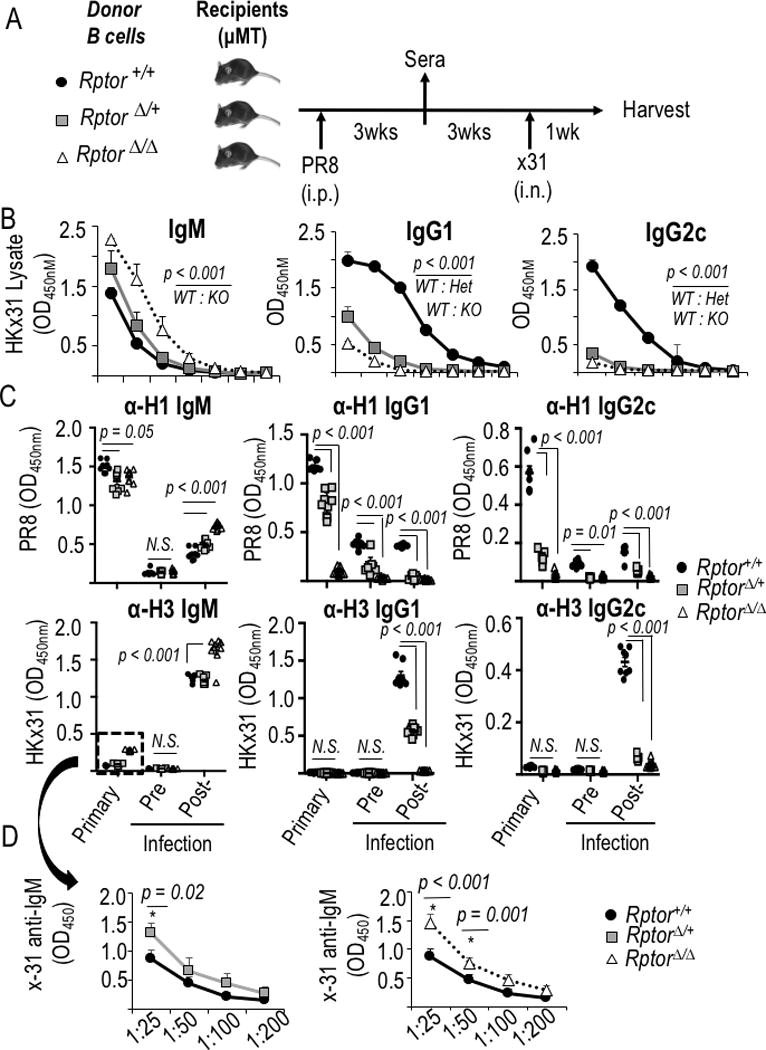
mTORC1 level programs the spectrum of anti-influenza Ab in primary and recall responses. (A) Schema of adoptive transfer, immunization, and respiratory challenge experiments to test B cell-intrinsic function of mTORC1 in humoral responses to influenza virus. Donor B cells were harvested from Rosa26-CreERT2 mice with wild-type or flox alleles of Rptor after tamoxifen injections as in Fig. 1A. (B) Mean (±SEM) ELISA results on sera 1 wk after PR8-immunized mice were challenged with intranasal X-31 strain influenza virus, using lysates of X-31 virions to capture anti-FLU Ab in sera from mice whose B cells were WT, haplo-insufficient for Rptor, or homozygous for the deleted Rptor allele. Isotype-specific ELISA results after serial two-fold dilutions starting at 1:50 serum dilution. For sera of WT versus Rptor-depleted B cell recipients, p≤0.001 by ANOVA calculated for each of the three isotypes as specified in the Methods, followed by pairwise comparisons at single dilutions. (C) Mean (±SEM) results of ELISA performed with recombinant HA proteins to capture anti-H1 (PR8) and anti-H3 (X-31) Ab of the indicated isotypes, using sera (1:100 dilutions) from the mice in (B) after identification of serum dilutions in the linear range of the assay. Data capture the sera from individual recipient mice for each genotype of donor B cells [8 Rptor +/+, 9 Rptor Δ/+, and 9 Rptor Δ/Δ, each distributed evenly among three independent experiments]. (D) Titrations for cross-reactive IgM anti-H3 in the primary response to immunization with A/PR8, separating panels comparing Δ/+ (left) and Δ / Δ (right) to the same WT controls for clarity. Significance testing was performed using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons, followed by testing the null hypothesis for pairwise comparisons at 1:25 dilutions.
