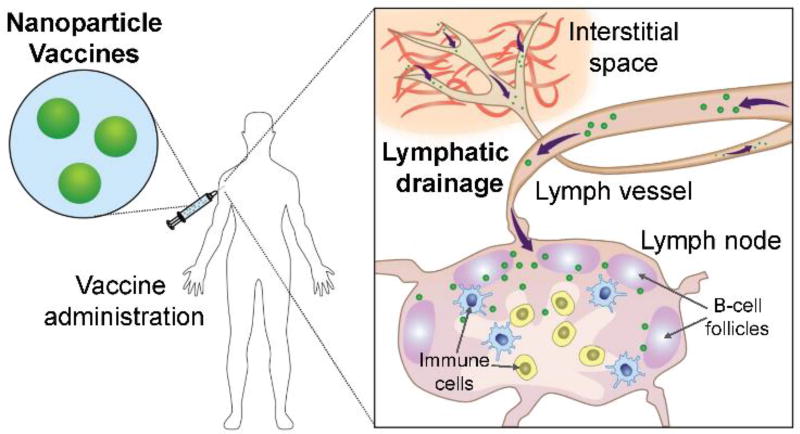
Figure 1.
Schematic of nanoparticle-based vaccine delivery and transport. Upon administration via the commonly employed subcutaneous route of delivery, the small size of the nanoparticles enables efficient drainage and transport to the lymph nodes. Here, the nanoparticles can deliver their payloads to activate the resident immune cells (i.e. dendritic cells, T cells, and B cells) and promote immunity.