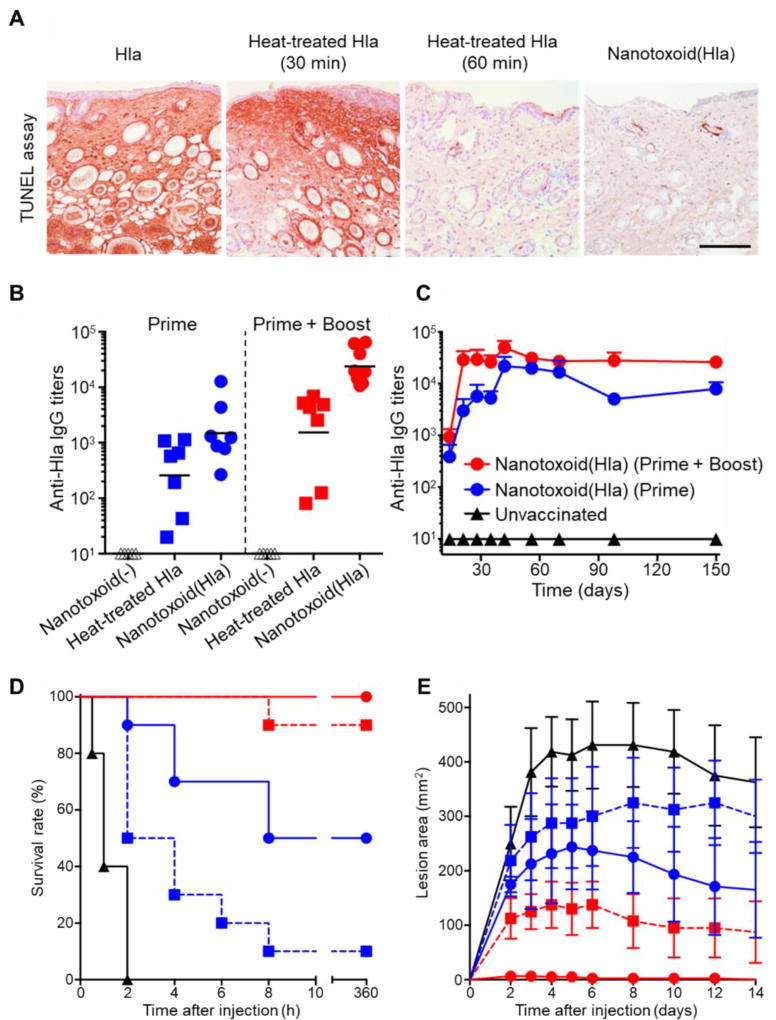
Figure 5.
Single-toxin nanotoxoid against staphylococcal α-hemolysin. (A) Nanoparticles detaining α-hemolysin (Hla), termed nanotoxoid(Hla), do not induce apoptosis when injected into the superficial dorsal skin of mice, while 60 minutes of treatment is necessary to achieve the same effect by heat denaturation at 70 °C (scale bar, 400 mm). (B) When used to vaccinate mice, nanotoxoid(Hla) induces higher anti-Hla titers than heat-treated Hla on a prime only or prime plus boost schedule. (C) The antibody titers elicited by the nanotoxoid(Hla) are long lasting, remaining stable for up to 150 days. (D) Nanotoxoid(Hla) protects against a bolus dose of Hla administered intravenously. (E) Nanotoxoid(Hla) prevents the formation of skin lesions when mice are subcutaneously challenged with Hla. Reprinted with permission from ref 73. Copyright 2013 Springer Nature.