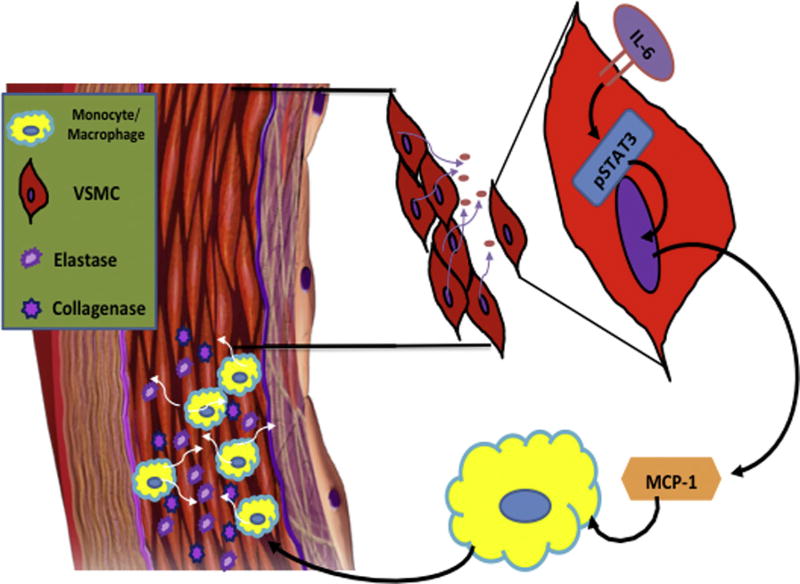
Fig. 5.
Hypothesized IL-6 pathway leading to early aortic remodeling. This model demonstrates a putative pathway whereby circulating IL-6 may bind to vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) IL-6 receptors, resulting in the phosphorylation of STAT3, which, once phosphorylated, will translocate into the nucleus and act as a transcription factor driving the production and subsequent secretion of the monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1). Secretion of MCP-1 may then stimulate migration and infiltration of monocytes/macrophages into the aortic wall, which secrete elastase and collagenase, contributing to vascular remodeling.