Fig. 4.
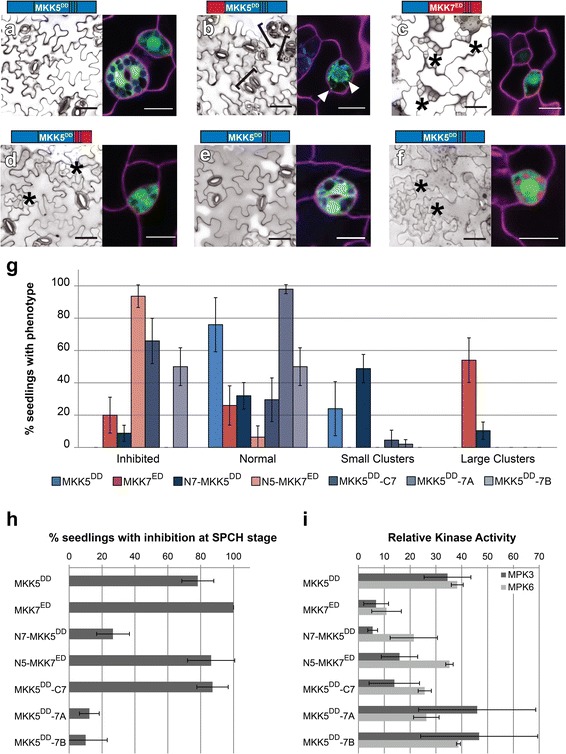
N-termini link MKKs to their phenotypic outputs and the C-terminal Loop B is required for FAMA stage-specific regulation of MKK5. a–f Paired micrographs of representative major phenotype (left) and subcellular localization (right), of specific MKK5DD- and MKK7ED-YFP variants (diagramed above). Black brackets mark clusters and asterisks indicate inhibition. YFP is in green and cell outlines in magenta. For example, in (a) MKK5DD expression results in a WT phenotype and the protein is cytoplasmic and in (b) mitochondrial/cytoplasmic N7-MKK5DD induces stomatal clustering. Mitochondria-localized signals indicated with white arrowheads. Scale bars are 50 μm in phenotype images and 10 μm for localization images. g Quantification of phenotypes in (a–f). h SPCH stage inhibition of lineage initiation. Error bars in (g) and (h) correspond to 95% confidence interval. i In vitro kinase activity towards kinase inactive MPK3 and MPK6. Kinase assays were performed in triplicates, normalized to unphosphorylated KI-MPK and averaged; error bars represent standard errors
