Fig. 9.
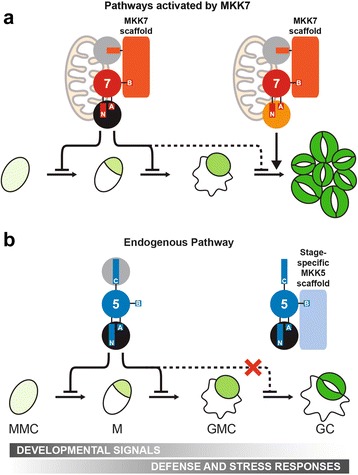
A new model derived from activities during stomatal development for the endogenous MKK5 pathway and another activated by MKK7. a In the MKK7 pathway, MKK7 mimics MKK5 in early development, forcing precursors to exit the stomatal lineage. At the last stage, MKK7 induces two phenotypes. Firstly, MKK7 induces stomatal clustering by means of an unknown MKK7-specific MPK (orange circle). This proliferation depends on MKK7 mitochondrial localization [23]. Secondly, MKK7 forces precursors to exit the lineage by escaping MKK5-specific regulation. An MKK7 scaffold enforces interactions between MKK7 and other components (MPKs and YODA, gray circles) within the network. b In the endogenous pathway, MKK5 and MPK3/6 (black circles) are involved in transducing developmental signals that inhibit stomatal lineage initiation and GMC commitment, and initiating defense and stress responses. At the last stage of development, a stage-specific MKK5 scaffold prevents MKK5 (and possibly MPK3/6) from inhibiting stomatal formation, only allowing defense and stress responses
