Fig. 2.
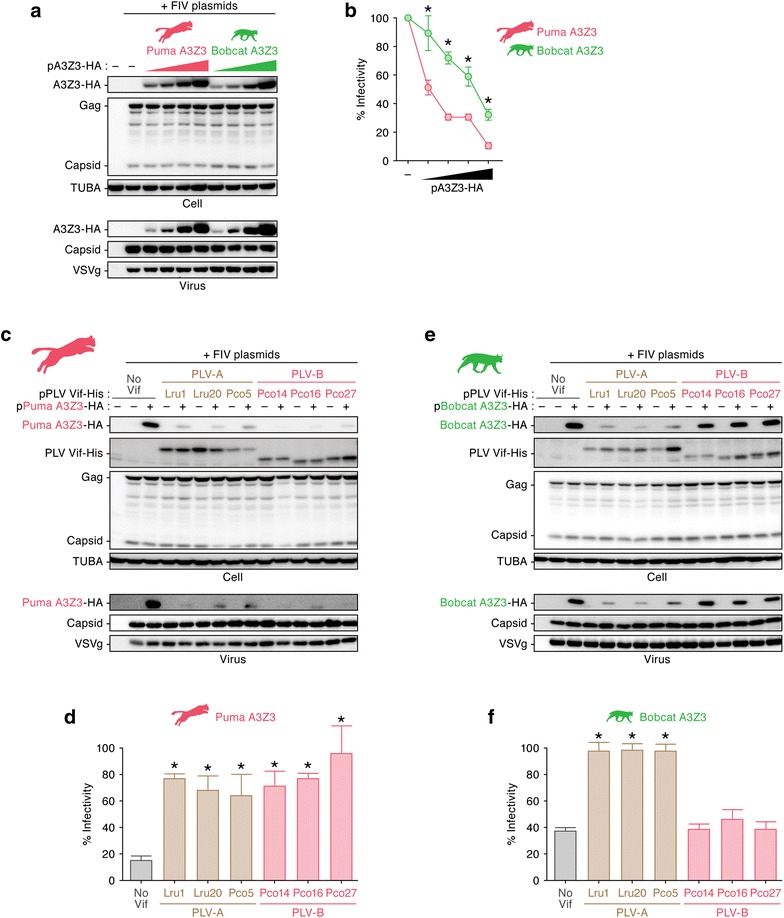
Resistance of bobcat A3Z3 to PLV-B Vif-dependent degradation. a, b Antiviral effects of the puma and bobcat A3Z3 proteins. Different amounts of HA-tagged expression plasmids for puma or bobcat A3Z3 (0, 50, 100, 200 and 400 ng) and the three plasmids used to produce the vif-deficient FIV-based reporter virus (FIV plasmids; pFP93 [200 ng], pTiger-luc [150 ng] and pMD.G [50 ng]) were co-transfected into HEK293T cells. a Western blotting. Representative results are shown. b FIV reporter assay. FIV infectivity is shown as the percentage of the value of “no A3Z3”. c–f Puma and bobcat A3Z3 sensitivity to PLV Vif. HA-tagged expression plasmids for puma (c, d) and bobcat (e, f) A3Z3 (200 ng) and the three plasmids used to produce the vif-deficient FIV-based reporter virus (FIV plasmids; pFP93 [200 ng], pTiger-luc [150 ng] and pMD.G [50 ng]) were co-transfected with or without His-tagged PLV Vif expression plasmids (400 ng) into HEK293T cells. c, e Western blotting. Representative results are shown. d, f FIV reporter assay. FIV infectivity is shown as the percentage of the value of “no A3Z3”. In b, asterisks indicate significant differences (P < 0.05 by Student’s t test) between puma A3Z3 and bobcat A3Z3. In d and f, asterisks indicate significant differences (P < 0.05 by Student’s t test) versus “no Vif”. The assays were independently performed in triplicate. Data represent averages with SDs
