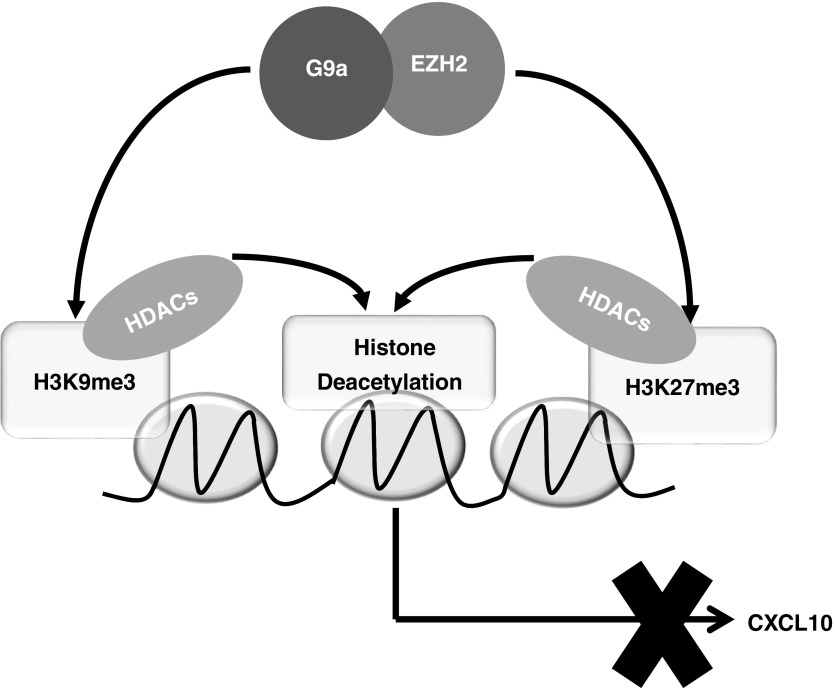
Figure 7.
A hypothetical model depicting the role of the interplay between EZH2 and G9a in the regulation of CXCL10 gene repression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. EZH2 and G9a physically and interdependently interact with each other in F-IPF. EZH2- and G9a-mediated H3K27me3 and H3K9me3 result in the recruitment of HDACs to the CXCL10 promoter. This then leads to histone deacetylation, causing reinforced epigenetic silencing of the CXCL10 gene in F-IPF. Inhibition or depletion of either EZH2 or G9a leads to the removal of repressive H3K27me3, H3K9me3, and histone deacetylation, resulting in chromatin derepression and CXCL10 gene reexpression in F-IPF.