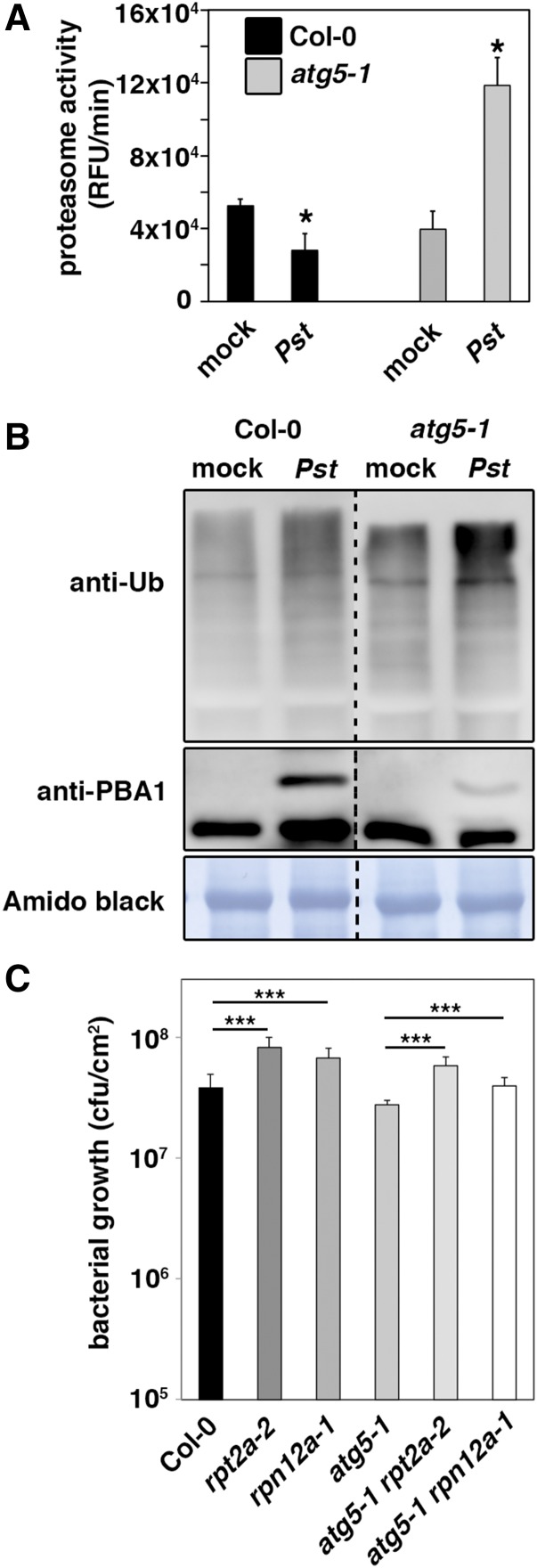
Figure 1.
Pst-Induced Proteasome Suppression Is Dependent on Autophagy.
(A) Proteasome activity in leaves of Col-0 and atg5-1 plants upon infection with either Pst wild-type bacteria or mock. Leaf samples were taken 1 d postinoculation (dpi), and the relative proteasome activity was determined. Bars represent means ± sd (n = 3 biological replicates). MgCl2 infiltration served as the mock control. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (*P < 0.05) determined by Student’s t test (compared with mock control). The experiment was repeated at least three times with similar results.
(B) Immunoblot analysis of the 20S proteasome subunit PBA1 and ubiquitinated proteins in Col-0 and atg5-1 leaves upon infection with Pst and mock. Total proteins were extracted from infiltrated leaves at 1 dpi, separated by SDS-PAGE, and probed with specific anti-PBA1 and anti-Ub antibodies. Mock-infected plants served as control, and amido black staining verified equal protein loading. Immunoblot analysis was reproduced at least three times with comparable results.
(C) Growth of Pst in 4- to 5-week-old Col-0, rpt2a-2, rpn12a-1, atg5-1, atg5-1 rpt2a-2, and atg5-1 rpn12a-1 plants 3 d after syringe infiltration at OD600 = 0.0001. Bars represent means ± sd (n = 4 biological replicates), and asterisks indicate statistical significance (***P < 0.001) determined by Student’s t test. The resistance assay was done twice with comparable results.