Fig. 1.
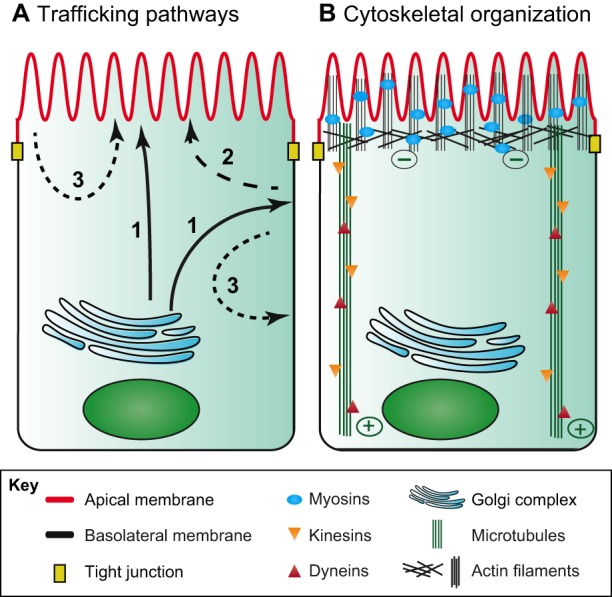
Schematic overview of the intestinal trafficking machinery. Schematics of polarized mouse enterocytes showing their cell features, cytoskeletal organization and trafficking routes. The apical surface is uppermost. (A) Apically and basolaterally destined proteins follow different pathways (denoted by arrows) to reach their target membrane. The biosynthetic route (route 1) is indicated in black line, the transcytotic route (route 2) in dashed line, and the recycling pathway (route 3) in dotted line. (B) Vesicle transport is mediated by the cytoskeleton. Long-distance transport occurs along microtubules, and is mediated by kinesin and dynein motor proteins. Short-distance transport occurs along actin filaments of the terminal web and is mediated by motor proteins of the myosin family.
