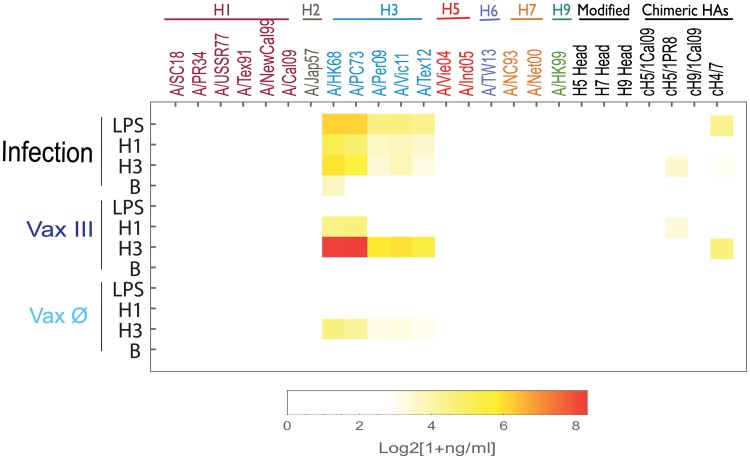
Fig 7. Comparison of anti-HA IgG from mouse spleen memory B cells (MBC) stimulated by infection with A/HongKong/1/1968 (A/HK68 H3N2) virus or vaccinated with adjuvanted rHA.
The anti-HA IgG levels in supernatants of stimulated memory B cells (MBC) cultures were determined by 29-plex panel mPlex-Flu assay. Briefly, mouse spleen MBCs were cultured for 6 days with 0.4 μg LPS (LPS), 10 μg BPL-inactivated A/Cal09 virus (H1) and B/Brisbane/60/2008 virus (B), 2009–2013 H3N2 viral antigen (H3), and medium control (Con), respectively. Influenza virus specific antibody concentrations present in the cell culture supernatants are shown as the mean of IgG concentrations after subtracting the control baseline antibodies in control unstimulated cell cultures (n = 3–4) and represented as a heatmap. The values of IgG concentrations without subtracting the control baseline antibodies in unstimulated cultures (Con), shown in Supplementary material (S7 Fig), demonstrate that only a low level of IgG antibodies produced by murine splenic B cells, after infection and vaccination, without stimulation.