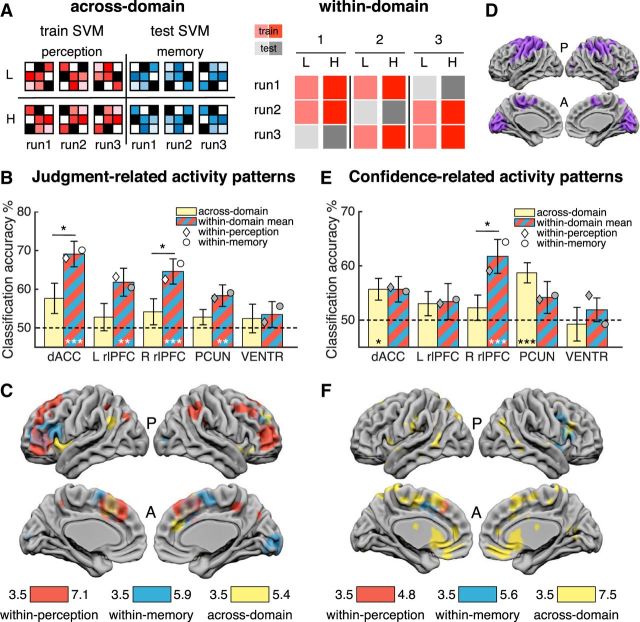
Figure 4.
MVPA results. Classification designs. A, Left, Across-domain classification design. Pattern vectors (runwise beta images) from one domain were used to train an SVM decoder on two classes and then tested in a cross-classification of the same two classes using vectors from the other domain (and vice versa). Classification of low (L) and high (H) confidence levels is illustrated. Right, Within-domain classification design. Pattern vectors of two classes (e.g., low and high confidence) pertaining to one domain were used to train a decoder in a leave-one-run-out design that was then tested in the left-out pair. The process was iterated three times to test pairs from every run. An identical, independent cross-validation was performed on vectors from the other domain. B, C, JR activity patterns. B, ROI results for across-domain (yellow) and mean within-domain (red-blue stripe) classification accuracy of Confidence vs Follow trials. C, Searchlight analysis for same classifications in B. D, Low-level visuomotor mask used in F (see main text and Materials and Methods for details). E, F, CLR activity patterns. E, Low versus high confidence classification accuracy results. F, Searchlight analysis for the same classifications in E exclusively masked for visuomotor-related activity patterns. Bars in B and E indicate means and error bars indicate SEM. Dashed lines indicate chance classification (50%). Diamonds and circles indicate mean independent classification in perception and memory trials, respectively. White diamonds/circles indicate classification was significantly different from chance, Bonferroni corrected. All clusters in C and F are significant at cluster-defining threshold p < 0.001, corrected for multiple comparisons at pFWE < 0.05. Image is displayed at p < 0.001. Color bars indicate T-scores. A, anterior; P, posterior. ***p ≤ 0.001; **p ≤ 0.01; *p < 0.05; all one-sample t tests are Bonferroni corrected.