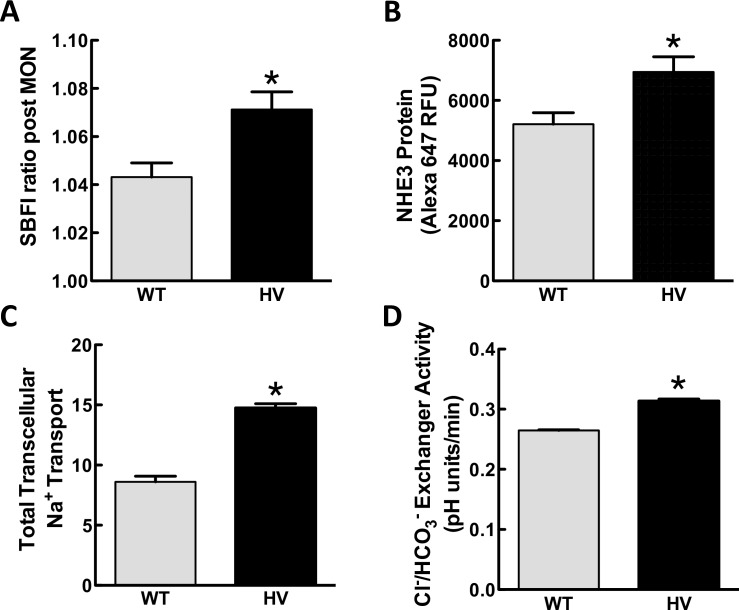
Fig 9. Ion transport assays in cultured hRPTCs carrying wild-type (WT) or homozygous variant (HV) SLC4A5.
A) Sodium accumulation assay. Intracellular sodium was measured in SBFI-loaded hRPTCs in response to monensin (MON, 10 μmol/L, 30 min). Monensin increases F340/F380 SBFI ratio to a greater extent in HV than WT SLC4A5 hRPTCs (N = 18, *P<0.005, t-test). B) NHE3 protein expression. Basal NHE3 protein expression is greater in HV than WT SLC4A5 hRPTCs (N = 48, *P<0.02, t-test). C) Transcellular sodium transport in polarized hRPTCs grown in Transwells™. Six HV SLC4A5 hRPTC lines derived from 6 different subjects and 4 WT SLC4A5 hRPTC lines derived from 4 different subjects were grown to confluence on Transwell™ membranes and until a stable trans-epithelial electrical resistance was achieved. Total sodium transport from the upper chamber (luminal) to the lower chamber (basolateral) was measured at 2 h as the amount of sodium measured by atomic absorption of samples taken from the lower chamber. Total sodium transport is greater in HV than WT SLC4A5 hRPTCs (N = 6–8, *P<0.01, t-test). D) Cl-/HCO- exchanger activity. The rate of pH recovery was measured after an alkaline load (CO2/HCO3- removal). Six HV SLC4A5 hRPTC cell lines derived from 6 different subjects (N = 4 experiments per subject) were compared with 4 WT SLC4A5 hRPTC lines derived from 4 different subjects (N = 4 experiments per subject). HV SLC4A5 hRPTCs have enhanced Cl-/HCO3- exchanger activity compared with WT SLC4A5 hRPTCs; rate of pH recovery is faster in hRPTCs carrying HV than WT SLC4A5 (*P<0.05, t-test).