Figure 1.
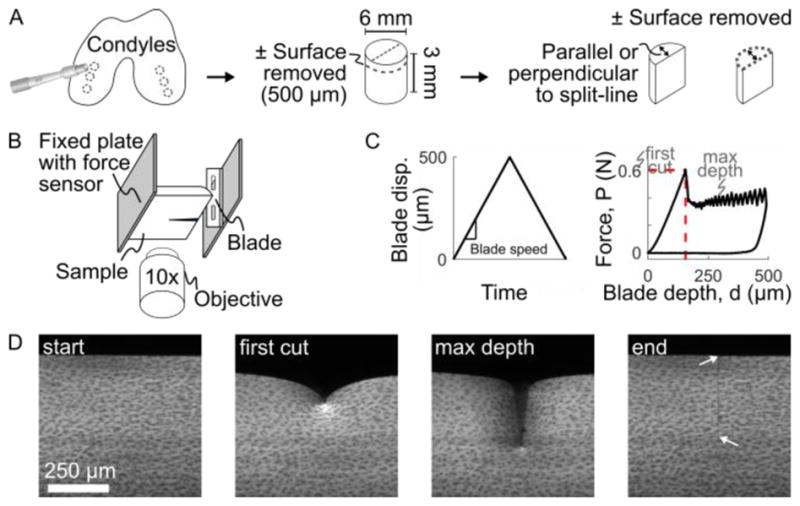
Outline of experimental methods. (A) Cylindrical plugs were harvested from medial and lateral condyles, trimmed to 3 mm deep, with the surface either intact or removed, and then bisected to create hemi-cylindrical samples. (B) Samples were mounted to the fixed plate of the test frame, with the cartilage surface facing the blade. The test frame was mounted on a confocal microscope to image local sample deformation. (C) The blade was driven into the sample at a fixed speed to a maximum displacement of 500 μm while the bulk force response was recorded at the fixed plate using a force sensor. A characteristic force-depth curve is shown with the point of first-cut marked by the dashed red lines. (D) Example confocal images taken throughout the experiment. At the end, after the blade has retracted, arrows mark the extent of the remaining crack. Note there is no residual deformation, indicating elastic deformation, other than the newly-created crack surface.
